凸优化:ADMM(Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers)交替方向乘子算法系列之二:Precursors
凸优化:ADMM(Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers)交替方向乘子算法系列之二:Precursors[本文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/shanglianlm/article/details/46808763]
最近开始对凸优化(convex optimization)中的ADMM(Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers)交替方向乘子算法开始感兴趣,接下来我会写一系列关于ADMM(Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers)交替方向乘子算法的内容。
凸优化:ADMM(Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers)交替方向乘子算法系列之二:Precursors
[本文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/shanglianlm/article/details/46808763]
2- 先导(Precursors)
2-1 对偶上升法(Dual Ascent)
设有如下优化问题:
它的拉格朗日形式为:
对偶形式为:
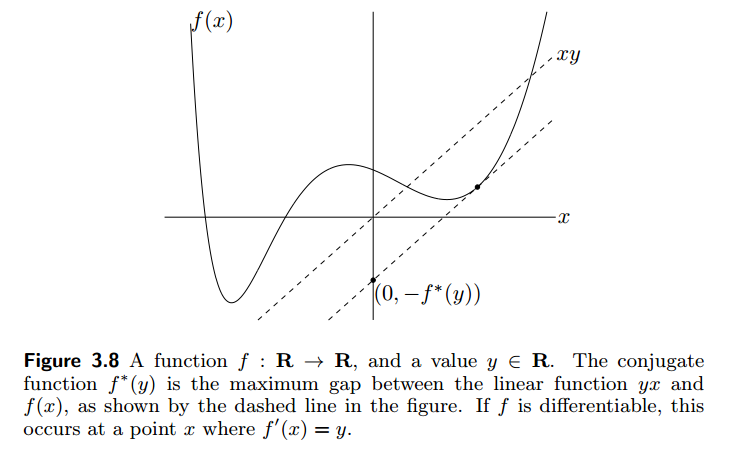
其中 f^* 是 f 的共轭函数。
The conjugate function
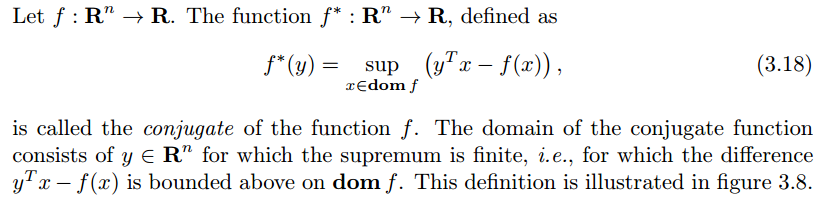
对偶问题为:
假设强对偶成立,原问题和对偶问题的最优值一样(Assuming that strong duality holds, the optimal values of the primal and dual problems are the same)。
对偶上升法的迭代更新为:
其中 αk>0 是步长。
2-2 对偶分解法(Dual Decomposition)
假设目标函数是可以分解的,即
因此,拉格朗日函数可以改写为:
所以它的迭代更新为:
2-3 增广拉格朗日(Augmented Lagrangians)
为了增加对偶上升法的鲁棒性和放松函数 f 的强凸约束,我们引入增广拉格朗日(Augmented Lagrangians)形式:
其中惩罚因子 ρ>0 。
与 (2.1) 式相比,(2.6) 式只是增加了一个惩罚项。
2-4 乘子法(Method of Multipliers)
对应于的迭代公式为:
我们称之为乘子法(Method of Multipliers)。
将拉格朗日应用于对偶上升法可以极大地增加它的收敛属性,但是它要求一些代价。当 f 可以分解,而拉格朗日 Lρ 不能分解的,因此 (13) 式不能对每个 xi 并行最小化。这意味着乘子法不能被用来分解。于是我们引出ADMM (见 下节)。
参考或延伸材料:
[1]Distributed Optimization and Statistical Learning via the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers
[2] 凸优化讲义
[3] A Note on the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容









所有评论(0)