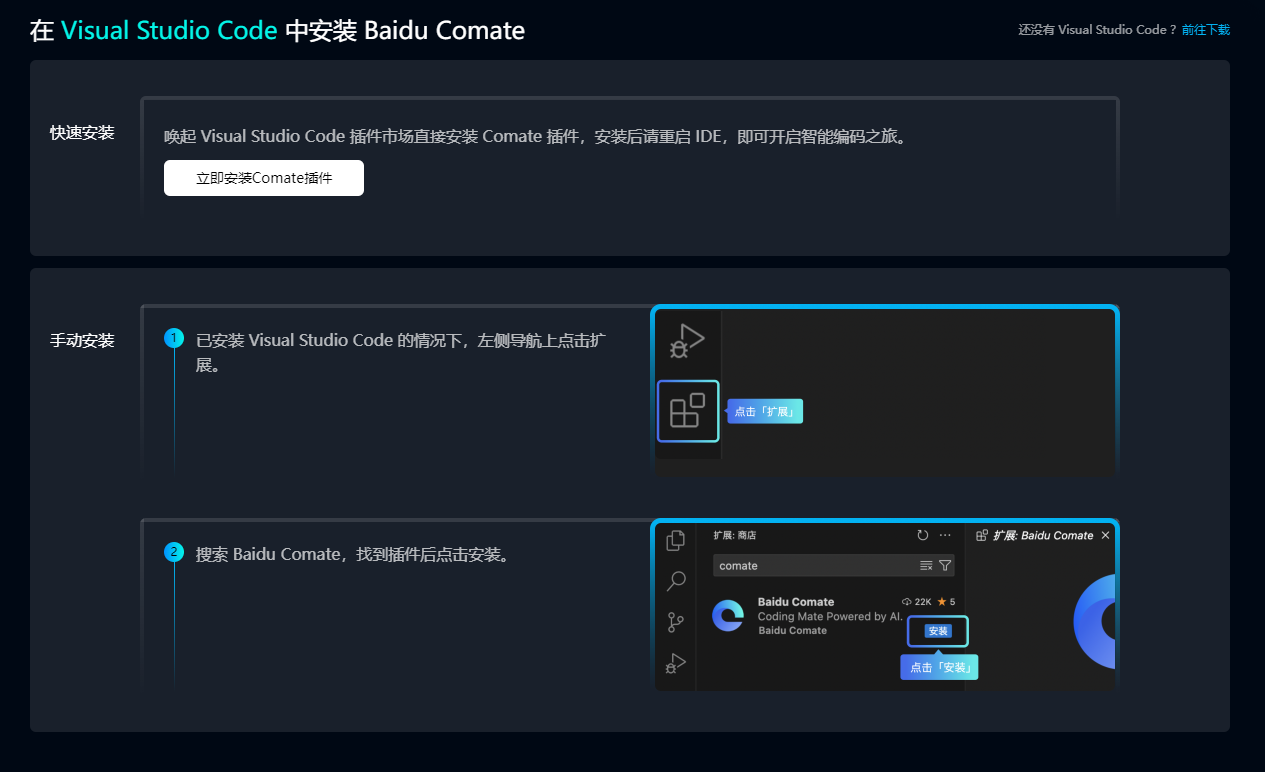
numpy与pytorch常用对应算子一览
记录了迁移时用到的numpy与pytorch的一些对应算子
最近将之前用numpy写的解码头合并写入了网络模型,于是顺便将迁移时用到的numpy与pytorch的一些对应算子记录于此
1. np.meshgrid 与 torch.meshgrid
作用:常用于坐标与网格的生成
numpy 中: X, Y = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x), np.arange(y)
若 x == 5 与 y == 4
则
X == np.array([[0., 1., 2., 3., 4.],
[0., 1., 2., 3., 4.],
[0., 1., 2., 3., 4.],
[0., 1., 2., 3., 4.]])
Y == np.array([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[2., 2., 2., 2., 2.],
[3., 3., 3., 3., 3.]])与之对应的
pytorch 中: Y, X = torch.meshgrid(torch.arange(y), torch.arange(x), indexing='ij')
2. np.concatenate 与 torch.cat
作用:矩阵(张量)间相互拼接
np.concatenate((a, b), axis=-1) 与 torch.cat((a, b), dim=-1) 效果相同
3. np.expand_dims 与 torch.unsqueeze
作用:矩阵(张量)的维度扩充
np.expand_dims(x, axis=-1) 与 torch.unsqueeze(x, dim=-1) 效果相同
4. np.squeeze 与 torch.squeeze
作用:矩阵(张量)的无效维度缩减
np.squeeze(x, axis=-1) 与 torch.squeeze(x, dim=-1) 效果相同
5. np.split 与 torch.split 和 torch.chunk
作用:矩阵(张量)的拆分
试图在某一维上等分成x分时,np.split 与 torch.chunk 对应,即
np.split(array, x, axis=0) 与 torch.chunk(tensor, x, dim=0) 效果相同
试图在某一维上按x(一个列表,numpy中代表索引,pytorch中代表切分长度)切分时,np.split 与 torch.split 对应,即
np.split(array, [1, 3, 5], axis=0) 与 torch.split(tensor, [1, 2, 2, 1], dim=0) 效果相同
6. np.dot 与 torch.mm
作用:矩阵(张量)间的点乘 [a x b x c] · [c x d] = [a x b x d]
z = np.dot(x, y) & z = torch.mm(x, y)
两者在结果上可能存在转置关系(即可能需要.T),迁移时还需验证
7. np.cumsum 与 torch. cumsum
作用:矩阵自己按某一维度的累和,返回与自己形状相同的矩阵
np.cumsum(array, axis=0) 与 torch.cumsum(tensor, dim=0) 作用相同
累乘 np.cumprod 与 torch.cumprod 同理
8. array.repeat 与 tensor.repeat_interleave
作用:常用于矩阵的重复扩充,如扩充权值矩阵以自适应多维度的输入
array.repeat(t) 与 tensor.repeat_interleave(t) 效果相同, 其中t为重复次数
x = np.array([0, 1])
print(x.repeat(3))
>>> [0 0 0 1 1 1]后续会继续补充...
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)