AlexNet 模型原理及 pytorch 代码
1. 模型原理AlexNet包含8层变换,其中有5层卷积(中间另外有3层池化层)和2层全连接隐藏层,以及1个全连接输出层。2. 代码import timeimport torchfrom torch import nn, optimimport torchvisionimport syssys.path.append("..")import d2lzh_pytorch as d2ldevice =
·
1. 模型原理
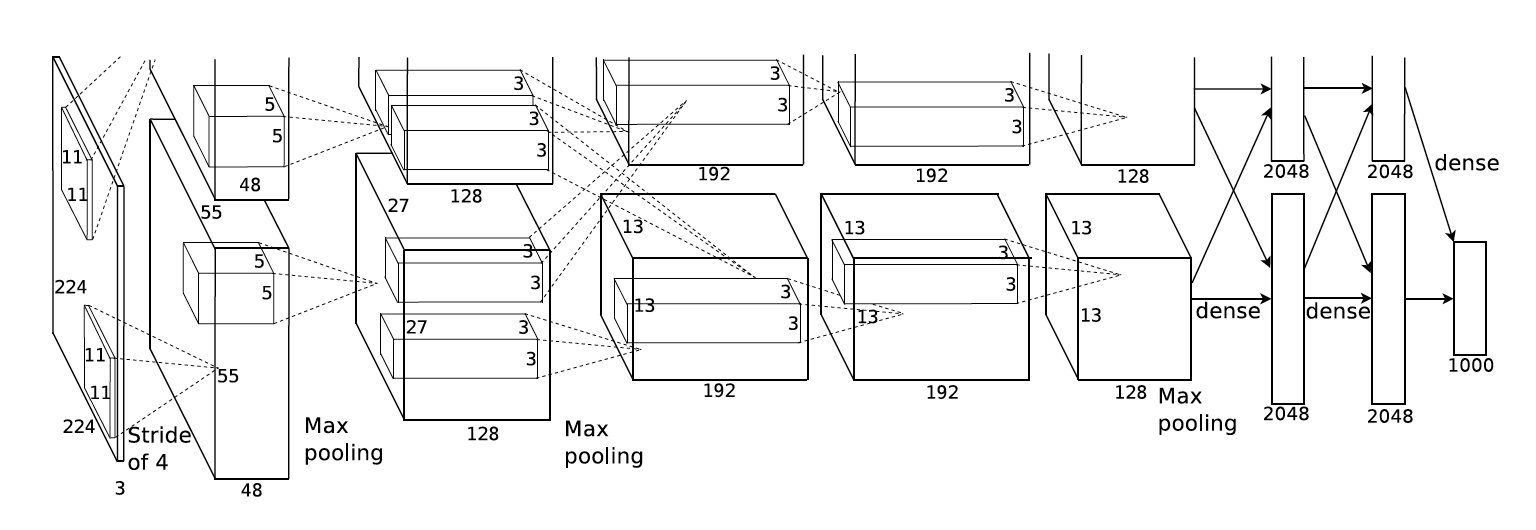
AlexNet包含8层变换,其中有5层卷积(中间另外有3层池化层)和2层全连接隐藏层,以及1个全连接输出层。
2. 代码
import time
import torch
from torch import nn, optim
import torchvision
import sys
sys.path.append("..")
import d2lzh_pytorch as d2l
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(AlexNet, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 96, 11, 4), # in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2), # kernel_size, stride
# 减小卷积窗口,使用填充为2来使得输入与输出的高和宽一致,且增大输出通道数
nn.Conv2d(96, 256, 5, 1, 2),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2),
# 连续3个卷积层,且使用更小的卷积窗口。除了最后的卷积层外,进一步增大了输出通道数。
# 前两个卷积层后不使用池化层来减小输入的高和宽
nn.Conv2d(256, 384, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 384, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2)
)
# 这里全连接层的输出个数比LeNet中的大数倍。使用丢弃层来缓解过拟合
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(256*5*5, 4096), # 全连接隐藏层
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096), # 全连接隐藏层
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
# 输出层。由于这里使用Fashion-MNIST,所以用类别数为10,而非论文中的1000
nn.Linear(4096, 10), # 全连接输出层
)
def forward(self, img):
feature = self.conv(img)
output = self.fc(feature.view(img.shape[0], -1))
return output
打印网络结构
net = AlexNet()
print(net)
输出:
AlexNet(
(conv): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(1, 96, kernel_size=(11, 11), stride=(4, 4))
(1): ReLU()
(2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(3): Conv2d(96, 256, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(4): ReLU()
(5): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(6): Conv2d(256, 384, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(7): ReLU()
(8): Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(9): ReLU()
(10): Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(11): ReLU()
(12): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(fc): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=6400, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(1): ReLU()
(2): Dropout(p=0.5)
(3): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(4): ReLU()
(5): Dropout(p=0.5)
(6): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
)
总结
- AlexNet跟LeNet结构类似,但使用了更多的卷积层和更大的参数空间来拟合大规模数据集ImageNet。它是浅层神经网络和深度神经网络的分界线。
- 虽然看上去AlexNet的实现比LeNet的实现也就多了几行代码而已,但这个观念上的转变和真正优秀实验结果的产生令学术界付出了很多年。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容









所有评论(0)