Claude Code 完整手册:从入门、配置到高级自动化
恭喜您完成了这份《Claude Code指南》的学习。通过本指南,您已经全面了解了如何从零开始安装、配置并在各种场景下高效使用 Claude Code 这一前沿的 AI 编程工具。我们共同探索了其丰富的功能,从基本的代码问答、文件编辑,到如自动化代码审查、安全漏洞扫描等高级的自动化与集成能力。更重要的是,您掌握了如何通过环境变量、配置文件、子代理以及强大的钩子系统(Hooks System)来深度

内容
Getting Started
Enable sound alerts when claude completes the task:
claude config set --global preferredNotifChannel terminal_bell
Quick Start
[!TIP]
Send claude or npx claude in terminal to start the interfaceGo to Help & Troubleshooting to fix issues…
# Node.js 18+⭐️
/*Universal Method */ npm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Windows
/* Via CMD */ npm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
/* Via Powershell */ irm https://claude.ai/install.ps1 | iex
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# WSL/GIT
/* Via Terminal */ npm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
/* Via Terminal */ curl -fsSL https://claude.ai/install.sh | bash
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# MacOS */ brew install node && npm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Linux
/* Via Terminal */ sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y nodejs npm
/* Via Terminal */ npm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
/* Via Terminal */ curl -fsSL https://claude.ai/install.sh | bash
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Arch
/* Via Terminal */ yay -S claude-code*/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Docker
/* Windows (CMD) */ docker run -it --rm -v "%cd%:/workspace" -e ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="sk-your-key" node:20-slim bash -lc "npm i -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code && cd /workspace && claude"
/* macOS/Linux (bash/zsh)*/ docker run -it --rm -v "$PWD:/workspace" -e ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="sk-your-key" node:20-slim bash -lc 'npm i -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code && cd /workspace && claude'
/* No bash Fallback */ docker run -it --rm -v "$PWD:/workspace" -e ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="sk-your-key" node:20-slim sh -lc 'npm i -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code && cd /workspace && claude'
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Check if claude is installed correctly
/* Linux */ which claude
/* Windows */ where claude
/* Universal */ claude --version
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Common Management
/*claude config */ Configure settings
/*claude mcp list */ Setup MCP servers, you can also replace "list" with add/remove
/*claude /agents */ Configure/Setup Subagents for different tasks
/*claude update */ Update to latest
[!Tip]
Open Project Via Terminal Into VS Code / Cursor$ - cd /path/to/project
$ - code .
Make sure you have the (Claude Code extension) installed in your VS Code / Cursor
System Requirements
- OS: macOS 10.15+, Ubuntu 20.04+/Debian 10+, or Windows 10/11 or WSL
- Hardware: 4GB RAM minimum 8GB+ recommended
- Software: Node.js 18+ or git 2.23+ (optional) & GitHub or GitLab CLI for PR workflows (optional)
- Internet: Connection for API calls
- Node.js 18+
Initial Setup
[!Tip]
Find API key from Anthropic ConsoleDo NOT commit real keys use git-ignored files, OS key stores, or secret managers
# Universal
/* start login process */ claude /login
/* Setup long-lived authentication token */ claude setup-token
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Windows
/* Set-api-key */ set ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=sk-your-key-here-here
/* cmd-masked-check */ echo OK: %ANTHROPIC_API_KEY:~0,8%***
/* Set-persistent-key */ setx ANTHROPIC_API_KEY "sk-your-key-here-here"
/* cmd-unset-key */ set ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Linux
/* Set-api-key */ export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="sk-your-key-here-here"
/* masked-check */ echo "OK: ${ANTHROPIC_API_KEY:0:8}***"
/* remove-session */ unset ANTHROPIC_API_KEY
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Powershell
/* ps-session */ $env:ANTHROPIC_API_KEY = "sk-your-key-here-here"
/* ps-masked-check */ "OK: $($env:ANTHROPIC_API_KEY.Substring(0,8))***"
/* ps-persist */ [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY","sk-your-key-here-here","User")
/* ps-rotate */ $env:ANTHROPIC_API_KEY = "sk-new-key"
/* ps-remove */ Remove-Item Env:\ANTHROPIC_API_KEY
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Other...
# persist-bash/* */ echo 'export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="sk-your-key-here-here"' >> ~/.bashrc && source ~/.bashrc
# persist-zsh /* */ echo 'export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="sk-your-key-here-here"' >> ~/.zshrc && source ~/.zshrc
# persist-fish/* */ fish -lc 'set -Ux ANTHROPIC_API_KEY sk-your-key-here-here'
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Configuration & Environment
Environment Variables
You can also set any of these in settings.json under the “env” key for automatic application.
[!Important]
Windows Users replace export with set or setx for perm
# Environment toggles (put in ~/.bashrc or ~/.zshrc)
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="sk-your-key-here-here" # API key sent as X-Api-Key header (interactive usage: /login)
export ANTHROPIC_AUTH_TOKEN="my-auth-token" # Custom Authorization header; Claude adds "Bearer " prefix automatically
export ANTHROPIC_CUSTOM_HEADERS="X-Trace-Id: 12345" # Extra request headers (format: "Name: Value")
export ANTHROPIC_MODEL="claude-sonnet-4-20250514" # Custom model name to use
export ANTHROPIC_DEFAULT_SONNET_MODEL="claude-sonnet-4-20250514" # Default Sonnet model alias
export ANTHROPIC_DEFAULT_OPUS_MODEL="claude-opus-4-20250514" # Default Opus model alias
export ANTHROPIC_SMALL_FAST_MODEL="haiku-model" # Haiku-class model for background tasks (placeholder)
export ANTHROPIC_SMALL_FAST_MODEL_AWS_REGION="REGION" # Override AWS region for the small/fast model on Bedrock (placeholder)
export AWS_BEARER_TOKEN_BEDROCK="bedrock_..." # Amazon Bedrock API key/token for authentication
export BASH_DEFAULT_TIMEOUT_MS=60000 # Default timeout (ms) for long-running bash commands
export BASH_MAX_TIMEOUT_MS=300000 # Maximum timeout (ms) allowed for long-running bash commands
export BASH_MAX_OUTPUT_LENGTH=20000 # Max characters in bash outputs before middle-truncation
export CLAUDE_BASH_MAINTAIN_PROJECT_WORKING_DIR=1 # (0 or 1) return to original project dir after each Bash command
export CLAUDE_CODE_API_KEY_HELPER_TTL_MS=600000 # Interval (ms) to refresh creds when using apiKeyHelper
export CLAUDE_CODE_IDE_SKIP_AUTO_INSTALL=1 # (0 or 1) skip auto-installation of IDE extensions
export CLAUDE_CODE_MAX_OUTPUT_TOKENS=4096 # Max number of output tokens for most requests
export CLAUDE_CODE_USE_BEDROCK=1 # (0 or 1) use Amazon Bedrock
export CLAUDE_CODE_USE_VERTEX=0 # (0 or 1) use Google Vertex AI
export CLAUDE_CODE_SKIP_BEDROCK_AUTH=0 # (0 or 1) skip AWS auth for Bedrock (e.g., via LLM gateway)
export CLAUDE_CODE_SKIP_VERTEX_AUTH=0 # (0 or 1) skip Google auth for Vertex (e.g., via LLM gateway)
export CLAUDE_CODE_DISABLE_NONESSENTIAL_TRAFFIC=0 # (0 or 1) disable nonessential traffic (equivalent to DISABLE_* below)
export CLAUDE_CODE_DISABLE_TERMINAL_TITLE=0 # (0 or 1) disable automatic terminal title updates
export DISABLE_AUTOUPDATER=0 # (0 or 1) disable automatic updates (overrides autoUpdates setting)
export DISABLE_BUG_COMMAND=0 # (0 or 1) disable the /bug command
export DISABLE_COST_WARNINGS=0 # (0 or 1) disable cost warning messages
export DISABLE_ERROR_REPORTING=0 # (0 or 1) opt out of Sentry error reporting
export DISABLE_NON_ESSENTIAL_MODEL_CALLS=0 # (0 or 1) disable model calls for non-critical paths
export DISABLE_TELEMETRY=0 # (0 or 1) opt out of Statsig telemetry
export HTTP_PROXY="http://proxy:8080" # HTTP proxy server URL
export HTTPS_PROXY="https://proxy:8443" # HTTPS proxy server URL
export MAX_THINKING_TOKENS=0 # (0 or 1 to turn off/on) force a thinking budget for the model
export MCP_TIMEOUT=120000 # MCP server startup timeout (ms)
export MCP_TOOL_TIMEOUT=60000 # MCP tool execution timeout (ms)
export MAX_MCP_OUTPUT_TOKENS=25000 # Max tokens allowed in MCP tool responses (default 25000)
export USE_BUILTIN_RIPGREP=0 # (0 or 1) set 0 to use system-installed rg instead of bundled one
export VERTEX_REGION_CLAUDE_3_5_HAIKU="REGION" # Region override for Claude 3.5 Haiku on Vertex AI
export VERTEX_REGION_CLAUDE_3_5_SONNET="REGION" # Region override for Claude 3.5 Sonnet on Vertex AI
export VERTEX_REGION_CLAUDE_3_7_SONNET="REGION" # Region override for Claude 3.7 Sonnet on Vertex AI
export VERTEX_REGION_CLAUDE_4_0_OPUS="REGION" # Region override for Claude 4.0 Opus on Vertex AI
export VERTEX_REGION_CLAUDE_4_0_SONNET="REGION" # Region override for Claude 4.0 Sonnet on Vertex AI
export VERTEX_REGION_CLAUDE_4_1_OPUS="REGION" # Region override for Claude 4.1 Opus on Vertex AI
Global Config Options
claude config set -g theme dark # Theme: dark | light | light-daltonized | dark-daltonized
claude config set -g preferredNotifChannel iterm2_with_bell # Notification channel: iterm2 | iterm2_with_bell | terminal_bell | notifications_disabled
claude config set -g autoUpdates true # Auto-download & install updates (applied on restart)
claude config set -g verbose true # Show full bash/command outputs
claude config set -g includeCoAuthoredBy false # Omit "co-authored-by Claude" in git commits/PRs
claude config set -g forceLoginMethod console # Restrict login to Anthropic Console (API billing)
claude config set -g model "claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022" # Default model override
claude config set -g statusLine '{"type":"command","command":"~/.claude/statusline.sh"}' # Custom status line
claude config set -g enableAllProjectMcpServers true # Auto-approve all MCP servers from .mcp.json
claude config set -g enabledMcpjsonServers '["memory","github"]' # Approve specific MCP servers
claude config set -g disabledMcpjsonServers '["filesystem"]' # Reject specific MCP servers
[!Important]
Windows Users replace export with set
export DISABLE_AUTOUPDATER=1 # Turn off automatic updates globally (overrides autoUpdates)
export CLAUDE_CODE_DISABLE_NONESSENTIAL_TRAFFIC=1 # Disable nonessential traffic (equiv. to DISABLE_* toggles below)
export DISABLE_TELEMETRY=1 # Opt out of Statsig telemetry
export DISABLE_ERROR_REPORTING=1 # Opt out of Sentry error reporting
export DISABLE_BUG_COMMAND=1 # Disable the /bug command
export DISABLE_COST_WARNINGS=0 # Keep cost warnings (set 1 to hide)
export DISABLE_NON_ESSENTIAL_MODEL_CALLS=1 # Skip non-critical model calls (flavor text, etc.)
export CLAUDE_CODE_DISABLE_TERMINAL_TITLE=1 # Stop auto-updating terminal titles
export CLAUDE_BASH_MAINTAIN_PROJECT_WORKING_DIR=1 # Return to original project dir after each Bash command
export CLAUDE_CODE_IDE_SKIP_AUTO_INSTALL=1 # Skip auto-installation of IDE extensions
export USE_BUILTIN_RIPGREP=0 # Use system 'rg' (0) instead of bundled 'rg'
export MAX_THINKING_TOKENS=0 # (0 or 1 to turn off/on) force a thinking budget for the model
export CLAUDE_CODE_MAX_OUTPUT_TOKENS=4096 # Cap typical response size (example value)
export HTTP_PROXY="http://proxy.company:8080" # HTTP proxy (if needed)
export HTTPS_PROXY="https://proxy.company:8443" # HTTPS proxy (if needed)
Configuration Files
(Memory type) Claude Code offers four memory locations in a hierarchical structure, each serving a different purpose:
| Memory Type | Location | Purpose | Use Case Examples | Shared With |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise policy | macOS: /Library/Application Support/ClaudeCode/CLAUDE.mdLinux: /etc/claude-code/CLAUDE.mdWindows: C:\ProgramData\ClaudeCode\CLAUDE.md |
Organization-wide instructions managed by IT/DevOps | Company coding standards, security policies, compliance requirements | All users in organization |
| Project memory | ./CLAUDE.md |
Team-shared instructions for the project | Project architecture, coding standards, common workflows | Team members via source control |
| User memory | ~/.claude/CLAUDE.md |
Personal preferences for all projects | Code styling preferences, personal tooling shortcuts | Just you (all projects) |
| Project memory (local) | ./CLAUDE.local.md |
Personal project-specific preferences | (Deprecated, see below) Your sandbox URLs, preferred test data | Just you (current project) |
All memory files are automatically loaded into Claude Code’s context when launched. Files higher in the hierarchy take precedence and are loaded first, providing a foundation that more specific memories build upon.
Commands & Usage
Claude Commands
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
/add-dir |
Add additional working directories |
/agents |
Manage custom AI subagents for specialized tasks |
/bug |
Report bugs (sends conversation to Anthropic) |
/clear |
Clear conversation history |
/compact [instructions] |
Compact conversation with optional focus instructions |
/config |
View/modify configuration |
/cost |
Show token usage statistics and billing information |
/doctor |
Checks the health of your Claude Code installation |
/help |
Get usage help |
/init |
Initialize project with CLAUDE.md guide |
/login |
Switch Anthropic accounts |
/logout |
Sign out from your Anthropic account |
/mcp |
Manage MCP server connections and OAuth authentication |
/memory |
Edit CLAUDE.md memory files |
/model |
Select or change the AI model |
/permissions |
View or update tool permissions |
/pr_comments |
View pull request comments |
/review |
Request code review |
/status |
View account and system statuses |
/terminal-setup |
Install Shift+Enter key binding for newlines (iTerm2 and VSCode only) |
/vim |
Enter vim mode for alternating insert and command modes |
Command Line Flags
| Flag / Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
-d, --debug |
Enable debug mode (shows detailed debug output). | claude -d -p "query" |
--mcp-debug |
[DEPRECATED] MCP debug mode (shows MCP server errors). Use --debug instead. |
claude --mcp-debug |
--verbose |
Override verbose mode setting from config (shows expanded logging / turn-by-turn output). | claude --verbose |
-p, --print |
Print response and exit (useful for piping output). | claude -p "query" |
--output-format <format> |
Output format (only works with --print): text (default), json (single result), or stream-json (realtime streaming). |
claude -p "query" --output-format json |
--input-format <format> |
Input format (only works with --print): text (default) or stream-json (realtime streaming input). |
claude -p --output-format stream-json --input-format stream-json |
--replay-user-messages |
Re-emit user messages from stdin back to stdout for acknowledgment — only works with --input-format=stream-json and --output-format=stream-json. |
claude --input-format stream-json --output-format stream-json --replay-user-messages |
--allowedTools, --allowed-tools <tools...> |
Comma/space-separated list of tool names to allow (e.g. "Bash(git:*) Edit"). |
--allowed-tools "Bash(git:*)" Edit" |
--disallowedTools, --disallowed-tools <tools...> |
Comma/space-separated list of tool names to deny (e.g. "Bash(git:*) Edit"). |
--disallowed-tools "Edit" |
--mcp-config <configs...> |
Load MCP servers from JSON files or strings (space-separated). | claude --mcp-config ./mcp-servers.json |
--strict-mcp-config |
Only use MCP servers from --mcp-config, ignoring other MCP configurations. |
claude --mcp-config ./a.json --strict-mcp-config |
--append-system-prompt <prompt> |
Append a system prompt to the default system prompt (useful in print mode). | claude -p --append-system-prompt "Do X then Y" |
--permission-mode <mode> |
Permission mode for the session (choices include acceptEdits, bypassPermissions, default, plan). |
claude --permission-mode plan |
--permission-prompt-tool <tool> |
Specify an MCP tool to handle permission prompts in non-interactive mode. | claude -p --permission-prompt-tool mcp_auth_tool "query" |
--fallback-model <model> |
Enable automatic fallback to a specified model when the default is overloaded (note: only works with --print per help). |
claude -p --fallback-model claude-haiku-20240307 "query" |
--model <model> |
Model for the current session. Accepts aliases like sonnet/opus or a full model name (e.g. claude-sonnet-4-20250514). |
claude --model sonnet |
--settings <file-or-json> |
Load additional settings from a JSON file or a JSON string. | claude --settings ./settings.json |
--add-dir <directories...> |
Additional directories to allow tool access to. | claude --add-dir ../apps ../lib |
--ide |
Automatically connect to an IDE on startup if exactly one valid IDE is available. | claude --ide |
-c, --continue |
Continue the most recent conversation in the current directory. | claude --continue |
-r, --resume [sessionId] |
Resume a conversation; provide a session ID or interactively select one. | claude -r "abc123" |
--session-id <uuid> |
Use a specific session ID for the conversation (must be a valid UUID). | claude --session-id 123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000 |
--dangerously-skip-permissions |
Bypass all permission checks (only for trusted sandboxes). | claude --dangerously-skip-permissions |
-v, --version |
Show the installed claude CLI version. |
claude --version |
-h, --help |
Display help / usage. | claude --help |
The
--output-format jsonflag is particularly useful for scripting and automation, allowing you to parse Claude’s responses programmatically.
Cheat Sheet
## Claude Cheat Sheet
# Basics / interactive
claude # Start interactive REPL
claude "explain this project" # Start REPL seeded with a prompt
claude -p "summarize README.md" # Non-interactive print mode (SDK-backed)
cat logs.txt | claude -p "explain" # Pipe input to Claude and exit
claude -c # Continue most recent conversation (alias for --continue)
claude -r "<session-id>" "finish this" # Resume specific session by ID (alias for --resume)
claude --model claude-sonnet-4-20250514# Pick model for this run
claude --max-turns 3 -p "lint this" # Cap agentic turns in print mode
claude --replay-user-messages # Replay user messages to stdout for debugging / SDK workflows
# Update & install
claude update # Manually update Claude Code
claude doctor # Diagnose install/version & setup
claude install # Start native binary installer (beta)
claude migrate-installer # Migrate from global npm to local installer
# Config: interactive wizard + direct ops
claude config # Interactive config wizard
claude config get <key> # Get value (e.g., claude config get theme)
claude config set <key> <val> # Set value (e.g., claude config set theme dark)
claude config add <key> <vals…> # Append to array-type keys (e.g., claude config add env DEV=1)
claude config remove <key> <vals…> # Remove items from list-type keys
claude config list # Show all current settings for project (project scope is default)
# Example project-scoped settings
claude config set model "claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022" # Override default model for this project
claude config set includeCoAuthoredBy false # Disable "co-authored-by Claude" byline in git/PRs
claude config set forceLoginMethod claudeai # Restrict login flow: claudeai | console
claude config set enableAllProjectMcpServers true # Auto-approve all MCP servers from .mcp.json
claude config set defaultMode "acceptEdits" # Set default permission mode
claude config set disableBypassPermissionsMode disable # Prevent bypassPermissions mode (example key)
# Manage list settings (project scope)
claude config add enabledMcpjsonServers github # Approve a specific MCP server from .mcp.json
claude config add enabledMcpjsonServers memory # Add another
claude config remove enabledMcpjsonServers memory # Remove one entry
claude config add disabledMcpjsonServers filesystem # Explicitly reject a specific MCP server
# Global scope (use -g or --global)
claude config set -g autoUpdates false # Turn off automatic updates globally
claude config set --global preferredNotifChannel iterm2_with_bell
claude config set -g theme dark # Theme: dark | light | light-daltonized | dark-daltonized
claude config set -g verbose true # Show full bash/command outputs everywhere
claude config get -g theme # Confirm a global value
# MCP (Model Context Protocol) management
claude mcp # Launch MCP wizard / configure MCP servers
claude mcp list # List configured MCP servers
claude mcp get <name> # Show details for a server
claude mcp remove <name> # Remove a server
claude mcp add <name> <command> [args...] # Add local stdio server
claude mcp add --transport sse <name> <url> # Add remote SSE server
claude mcp add --transport http <name> <url> # Add remote HTTP server
claude mcp add <name> --env KEY=VALUE -- <cmd> [args...] # Pass env to server command
claude mcp add --transport sse private-api https://api.example/mcp \
--header "Authorization: Bearer TOKEN" # Add with auth header
claude mcp add-json <name> '<json>' # Add server via JSON blob
claude mcp add-from-claude-desktop # Import servers from Claude Desktop
claude mcp reset-project-choices # Reset approvals for project .mcp.json servers
claude mcp serve # Run Claude Code itself as an MCP stdio server
# Other useful flags (print / SDK mode)
claude --add-dir ../apps ../lib # Add additional working directories
claude --allowedTools "Bash(git log:*)" "Read" # Allow listed tools without permission prompts
claude --disallowedTools "Edit" # Disallow listed tools without permission prompts
claude --append-system-prompt "Custom instruction" # Append to system prompt (only with -p)
claude -p "query" --output-format json --input-format stream-json # Control IO formats for scripting
claude --verbose # Verbose logging (turn-by-turn)
claude --dangerously-skip-permissions # Skip permission prompts (use with caution)
# Quick verification / notes
# - Project scope is default for 'claude config'; use -g/--global to affect all projects.
# - Settings precedence: Enterprise > CLI args > local project > shared project > user (~/.claude).
# - Use 'add' / 'remove' only with list-type keys (e.g., enabledMcpjsonServers).
# - The CLI reference and release notes are the authoritative sources for flags and recent additions.
Interface & Input
Keyboard Shortcuts
| Shortcut | Description | Context |
|---|---|---|
Ctrl+C |
Cancel current input or generation | Standard interrupt |
Ctrl+D |
Exit Claude Code session | EOF signal |
Ctrl+L |
Clear terminal screen | Keeps conversation history |
Up/Down arrows |
Navigate command history | Recall previous inputs |
Esc + Esc |
Edit previous message | Double-escape to modify |
Multiline Input
| Method | Shortcut | Context |
|---|---|---|
| Quick escape | \ + Enter |
Works in all terminals |
| macOS default | Option+Enter |
Default on macOS |
| Terminal setup | Shift+Enter |
After /terminal-setup |
| Control sequence | Ctrl+J |
Line feed character for multiline |
| Paste mode | Paste directly | For code blocks, logs |
Quick Commands
| Shortcut | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
# at start |
Memory shortcut add to CLAUDE.md | Prompts for file selection |
/ at start |
Slash command |
Vim Mode
[!Note]
Enable vim-style editing with/vimcommand or configure permanently via/config.
Vim Mode Switching
| Command | Action | From mode |
|---|---|---|
Esc |
Enter NORMAL mode | INSERT |
i |
Insert before cursor | NORMAL |
I |
Insert at beginning of line | NORMAL |
a |
Insert after cursor | NORMAL |
A |
Insert at end of line | NORMAL |
o |
Open line below | NORMAL |
O |
Open line above | NORMAL |
Vim Navigation
| Command | Action |
|---|---|
h/j/k/l |
Move left/down/up/right |
w |
Next word |
e |
End of word |
b |
Previous word |
0 |
Beginning of line |
$ |
End of line |
^ |
First non-blank character |
gg |
Beginning of input |
G |
End of input |
Vim Editing
| Command | Action |
|---|---|
x |
Delete character |
dd |
Delete line |
D |
Delete to end of line |
dw/de/db |
Delete word/to end/back |
cc |
Change line |
C |
Change to end of line |
cw/ce/cb |
Change word/to end/back |
. |
Repeat last change |
[!Tip]
Configure your preferred line break behavior in terminal settings. Run/terminal-setupto install Shift+Enter binding for iTerm2 and VS Code terminals.
Command History
Claude Code maintains command history for the current session:
* History is stored per working directory
* Cleared with `/clear` command
* Use Up/Down arrows to navigate (see keyboard shortcuts above)
* **Ctrl+R**: Reverse search through history (if supported by terminal)
* **Note**: History expansion (`!`) is disabled by default
Advanced Features
Thinking Keywords
[!Note]
Gives Claude extra pre-answer planning time by adding ONE of these keywords to your prompt.
Order (lowest → highest) token consumption
think -------------> Lowest
think hard
think harder
ultrathink --------> Highest
This makes Claude spend more time:
- Planning the solution
-
breaking down steps
-
weighing alternatives/trade-offs
-
checking constraints & edge cases
Higher levels usually increase latency and token usage pick the smallest that works.
Examples
# Small boost
claude -p "Think. Outline a plan to refactor the auth module."
# Medium boost
claude -p "Think harder. Draft a migration plan from REST to gRPC."
# Max boost
claude -p "Ultrathink. Propose a step-by-step strategy to fix flaky payment tests and add guardrails."
Sub Agents
Sub‑Agents are purpose‑built helpers with their own prompts, tools, and isolated context windows. Treat this like a “mixture‑of‑experts” you compose per repo.
When to use them
- You need high signal responses (plans, reviews, diffs) without side quests.
- You want version‑controlled prompts and tool policies alongside the codebase.
- You work in PR‑driven teams and want scoped edits by role.
Each Sub‑Agent Has Its Own Context
Design rules for your lineup
- Define one clear responsibility per agent.
- Keep the minimum tool set needed for that role.
- Prefer read‑only agents for analysis/review tasks.
- Give edit powers to as few agents as possible.
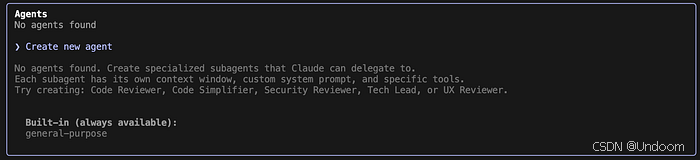
Caption: Agents selection UI in the terminal.
Configure Agents
Keep agents in the project so they’re versioned with the repo and evolve via PRs.
Quick start
Update CLI and open the agents panel
claude update
/agents
Create your core agents
- planner (read‑only): turns features/issues into small, testable tasks; outputs a task list or plan.md.
- codegen (edit‑capable): implements tasks; limited to
src/+tests/.- tester (read‑only or patch‑only): writes one failing test or a minimal repro.
- reviewer (read‑only): leaves structured review comments; never edits.
- docs (edit‑capable): updates
README.md/docs/only.
Policy tip: Prefer patch output for edit‑capable agents so changes land through your normal Git workflow.
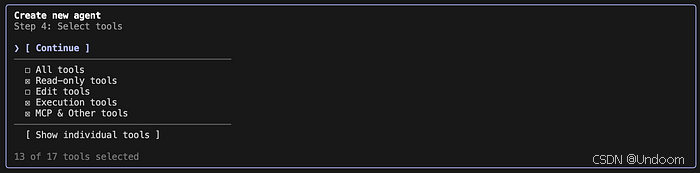
Caption: Choose only the tools an agent truly needs (e.g., advisory vs editing access).
Example prompts
Keep prompts short, testable, and repo‑specific. Check them into
agents/:
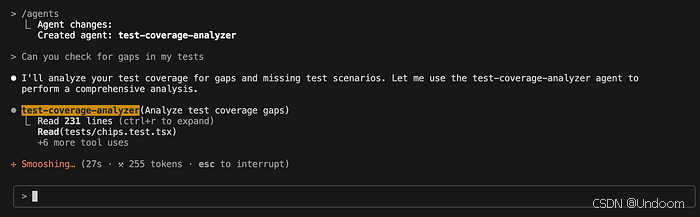
Caption: Example prompt for a test‑coverage‑analyzer agent.
tester.prompt.md (sample)
Role: Write a single, focused failing test for the specific scenario I describe.
Scope: Only create/modify tests under tests/. Do not change src/.
Output: A brief rationale + a unified diff or patch.
If the scenario is unclear, ask exactly one clarifying question.
Expected output
Your tester agent should produce a small diff or patch plus a short rationale:
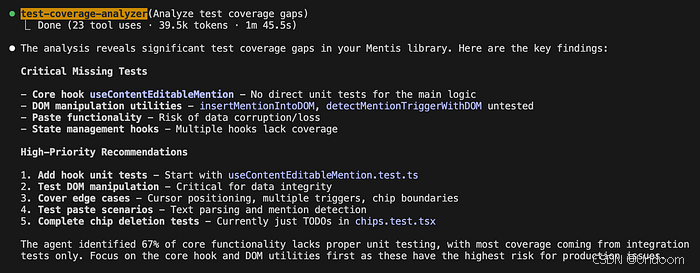
Caption: Example response from the test‑coverage‑analyzer agent.
Why This Shift Matters
Operational benefits
- Less context switching: you stay in one mental mode; agents do the rest.
- Cleaner PRs: narrow prompts + limited tools → smaller, reviewable diffs.
- Fewer regressions: tester/reviewer agents catch gaps before merge.
- Repeatability: prompts + policies live in the repo and travel with branches.
Security & governance
- Limit write access by path (e.g.,
src/,tests/,docs/).- Favor read‑only analysis for high‑risk areas.
- Log/commit assistant outputs as patches for auditability.
A Mindset Shift
Do
- Treat agents as teammates with job descriptions.
- Start read‑only; grant write access last.
- Keep prompts in version control and iterate via PR.
Don’t
- Ask one agent to plan, code, and test in a single turn.
- Give blanket write permissions.
- Accept multi‑file diffs when you asked for one test.
MCP Integration
Understanding MCP (Model Context Protocol)
What is MCP?
MCP extends Claude’s capabilities by connecting to external services, databases, APIs, and tools (filesystem, Puppeteer, GitHub, Context7 etc…)
MCP Architecture:
Claude Code ←→ MCP Protocol ←→ MCP Servers ←→ External Services
MCP Setup & Configuration
Basic MCP Commands
claude mcp # Interactive MCP configuration
claude mcp list # List configured servers
claude mcp add <name> <cmd> # Add new server
claude mcp remove <name> # Remove server
MCP Configuration File Location
~/.claude.json # Global File
`.mcp.json` # Project-scoped servers are stored in a File at your project's root directory
Popular MCP Servers
Development Tools
# npm install -g git-mcp-server
# claude mcp add git "git-mcp-server"
# claude mcp add github "github-mcp-server --token $GITHUB_TOKEN"
Database Integration
npm install -g postgres-mcp-server
npm install -g mysql-mcp-server
npm install -g sqlite-mcp-server
# Setup examples may look like this:
# export POSTGRES_URL="postgresql://user:password@localhost:5432/mydb"
# claude mcp add postgres "postgres-mcp-server --url $POSTGRES_URL"
MCP Tool Permissions
# Allow specific MCP tools
claude --allowedTools "mcp__git__commit,mcp__git__push"
# Allow all tools from specific server
claude --allowedTools "mcp__postgres__*"
# Combined with built-in tools
claude --allowedTools "Edit,View,mcp__git__*"
Hooks System
For a quickstart guide with examples, see [Get started with Claude Code hooks](/en/docs/claude-code/hooks-guide).This page provides reference documentation for implementing hooks in Claude Code.
Configuration
Claude Code hooks are configured in your settings files:
~/.claude/settings.json- User settings.claude/settings.json- Project settings.claude/settings.local.json- Local project settings (not committed)- Enterprise managed policy settings
Structure
Hooks are organized by matchers, where each matcher can have multiple hooks:
{
"hooks": {
"EventName": [
{
"matcher": "ToolPattern",
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "your-command-here"
}
]
}
]
}
}
- matcher: Pattern to match tool names, case-sensitive (only applicable for
PreToolUseandPostToolUse)- Simple strings match exactly:
Writematches only the Write tool - Supports regex:
Edit|WriteorNotebook.* - Use
*to match all tools. You can also use empty string ("") or leavematcherblank.
- Simple strings match exactly:
- hooks: Array of commands to execute when the pattern matches
type: Currently only"command"is supportedcommand: The bash command to execute (can use$CLAUDE_PROJECT_DIR
environment variable)timeout: (Optional) How long a command should run, in seconds, before
canceling that specific command.
For events like UserPromptSubmit, Notification, Stop, and SubagentStop
that don’t use matchers, you can omit the matcher field:
{
"hooks": {
"UserPromptSubmit": [
{
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "/path/to/prompt-validator.py"
}
]
}
]
}
}
Project-Specific Hook Scripts
You can use the environment variable CLAUDE_PROJECT_DIR (only available when
Claude Code spawns the hook command) to reference scripts stored in your project,
ensuring they work regardless of Claude’s current directory:
{
"hooks": {
"PostToolUse": [
{
"matcher": "Write|Edit",
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "$CLAUDE_PROJECT_DIR/.claude/hooks/check-style.sh"
}
]
}
]
}
}
Hook Events
PreToolUse
Runs after Claude creates tool parameters and before processing the tool call.
Common matchers:
Task- Subagent tasks (see subagents documentation)Bash- Shell commandsGlob- File pattern matchingGrep- Content searchRead- File readingEdit,MultiEdit- File editingWrite- File writingWebFetch,WebSearch- Web operations
PostToolUse
Runs immediately after a tool completes successfully.
Recognizes the same matcher values as PreToolUse.
Notification
Runs when Claude Code sends notifications. Notifications are sent when:
- Claude needs your permission to use a tool. Example: “Claude needs your
permission to use Bash” - The prompt input has been idle for at least 60 seconds. “Claude is waiting
for your input”
UserPromptSubmit
Runs when the user submits a prompt, before Claude processes it. This allows you
to add additional context based on the prompt/conversation, validate prompts, or
block certain types of prompts.
Stop
Runs when the main Claude Code agent has finished responding. Does not run if
the stoppage occurred due to a user interrupt.
SubagentStop
Runs when a Claude Code subagent (Task tool call) has finished responding.
PreCompact
Runs before Claude Code is about to run a compact operation.
Matchers:
manual- Invoked from/compactauto- Invoked from auto-compact (due to full context window)
SessionStart
Runs when Claude Code starts a new session or resumes an existing session (which
currently does start a new session under the hood). Useful for loading in
development context like existing issues or recent changes to your codebase.
Matchers:
startup- Invoked from startupresume- Invoked from--resume,--continue, or/resumeclear- Invoked from/clear
Hook Input
Hooks receive JSON data via stdin containing session information and
event-specific data:
{
// Common fields
session_id: string
transcript_path: string // Path to conversation JSON
cwd: string // The current working directory when the hook is invoked
// Event-specific fields
hook_event_name: string
...
}
PreToolUse Input
The exact schema for tool_input depends on the tool.
{
"session_id": "abc123",
"transcript_path": "/Users/.../.claude/projects/.../00893aaf-19fa-41d2-8238-13269b9b3ca0.jsonl",
"cwd": "/Users/...",
"hook_event_name": "PreToolUse",
"tool_name": "Write",
"tool_input": {
"file_path": "/path/to/file.txt",
"content": "file content"
}
}
PostToolUse Input
The exact schema for tool_input and tool_response depends on the tool.
{
"session_id": "abc123",
"transcript_path": "/Users/.../.claude/projects/.../00893aaf-19fa-41d2-8238-13269b9b3ca0.jsonl",
"cwd": "/Users/...",
"hook_event_name": "PostToolUse",
"tool_name": "Write",
"tool_input": {
"file_path": "/path/to/file.txt",
"content": "file content"
},
"tool_response": {
"filePath": "/path/to/file.txt",
"success": true
}
}
Notification Input
{
"session_id": "abc123",
"transcript_path": "/Users/.../.claude/projects/.../00893aaf-19fa-41d2-8238-13269b9b3ca0.jsonl",
"cwd": "/Users/...",
"hook_event_name": "Notification",
"message": "Task completed successfully"
}
UserPromptSubmit Input
{
"session_id": "abc123",
"transcript_path": "/Users/.../.claude/projects/.../00893aaf-19fa-41d2-8238-13269b9b3ca0.jsonl",
"cwd": "/Users/...",
"hook_event_name": "UserPromptSubmit",
"prompt": "Write a function to calculate the factorial of a number"
}
Stop and SubagentStop Input
stop_hook_active is true when Claude Code is already continuing as a result of
a stop hook. Check this value or process the transcript to prevent Claude Code
from running indefinitely.
{
"session_id": "abc123",
"transcript_path": "~/.claude/projects/.../00893aaf-19fa-41d2-8238-13269b9b3ca0.jsonl",
"hook_event_name": "Stop",
"stop_hook_active": true
}
PreCompact Input
For manual, custom_instructions comes from what the user passes into/compact. For auto, custom_instructions is empty.
{
"session_id": "abc123",
"transcript_path": "~/.claude/projects/.../00893aaf-19fa-41d2-8238-13269b9b3ca0.jsonl",
"hook_event_name": "PreCompact",
"trigger": "manual",
"custom_instructions": ""
}
SessionStart Input
{
"session_id": "abc123",
"transcript_path": "~/.claude/projects/.../00893aaf-19fa-41d2-8238-13269b9b3ca0.jsonl",
"hook_event_name": "SessionStart",
"source": "startup"
}
Hook Output
There are two ways for hooks to return output back to Claude Code. The output
communicates whether to block and any feedback that should be shown to Claude
and the user.
Simple: Exit Code
Hooks communicate status through exit codes, stdout, and stderr:
- Exit code 0: Success.
stdoutis shown to the user in transcript mode
(CTRL-R), except forUserPromptSubmitandSessionStart, where stdout is
added to the context. - Exit code 2: Blocking error.
stderris fed back to Claude to process
automatically. See per-hook-event behavior below. - Other exit codes: Non-blocking error.
stderris shown to the user and
execution continues.
Exit Code 2 Behavior
| Hook Event | Behavior |
|---|---|
PreToolUse |
Blocks the tool call, shows stderr to Claude |
PostToolUse |
Shows stderr to Claude (tool already ran) |
Notification |
N/A, shows stderr to user only |
UserPromptSubmit |
Blocks prompt processing, erases prompt, shows stderr to user only |
Stop |
Blocks stoppage, shows stderr to Claude |
SubagentStop |
Blocks stoppage, shows stderr to Claude subagent |
PreCompact |
N/A, shows stderr to user only |
SessionStart |
N/A, shows stderr to user only |
Advanced: JSON Output
Hooks can return structured JSON in stdout for more sophisticated control:
Common JSON Fields
All hook types can include these optional fields:
{
"continue": true, // Whether Claude should continue after hook execution (default: true)
"stopReason": "string" // Message shown when continue is false
"suppressOutput": true, // Hide stdout from transcript mode (default: false)
}
If continue is false, Claude stops processing after the hooks run.
- For
PreToolUse, this is different from"permissionDecision": "deny", which
only blocks a specific tool call and provides automatic feedback to Claude. - For
PostToolUse, this is different from"decision": "block", which
provides automated feedback to Claude. - For
UserPromptSubmit, this prevents the prompt from being processed. - For
StopandSubagentStop, this takes precedence over any"decision": "block"output. - In all cases,
"continue" = falsetakes precedence over any"decision": "block"output.
stopReason accompanies continue with a reason shown to the user, not shown
to Claude.
PreToolUse Decision Control
PreToolUse hooks can control whether a tool call proceeds.
"allow"bypasses the permission system.permissionDecisionReasonis shown
to the user but not to Claude. (Deprecated"approve"value +reasonhas
the same behavior.)"deny"prevents the tool call from executing.permissionDecisionReasonis
shown to Claude. ("block"value +reasonhas the same behavior.)"ask"asks the user to confirm the tool call in the UI.permissionDecisionReasonis shown to the user but not to Claude.
{
"hookSpecificOutput": {
"hookEventName": "PreToolUse",
"permissionDecision": "allow" | "deny" | "ask",
"permissionDecisionReason": "My reason here (shown to user)"
},
"decision": "approve" | "block" | undefined, // Deprecated for PreToolUse but still supported
"reason": "Explanation for decision" // Deprecated for PreToolUse but still supported
}
PostToolUse Decision Control
PostToolUse hooks can control whether a tool call proceeds.
"block"automatically prompts Claude withreason.undefineddoes nothing.reasonis ignored.
{
"decision": "block" | undefined,
"reason": "Explanation for decision"
}
UserPromptSubmit Decision Control
UserPromptSubmit hooks can control whether a user prompt is processed.
"block"prevents the prompt from being processed. The submitted prompt is
erased from context."reason"is shown to the user but not added to context.undefinedallows the prompt to proceed normally."reason"is ignored."hookSpecificOutput.additionalContext"adds the string to the context if not
blocked.
{
"decision": "block" | undefined,
"reason": "Explanation for decision",
"hookSpecificOutput": {
"hookEventName": "UserPromptSubmit",
"additionalContext": "My additional context here"
}
}
Stop/SubagentStop Decision Control
Stop and SubagentStop hooks can control whether Claude must continue.
"block"prevents Claude from stopping. You must populatereasonfor Claude
to know how to proceed.undefinedallows Claude to stop.reasonis ignored.
{
"decision": "block" | undefined,
"reason": "Must be provided when Claude is blocked from stopping"
}
SessionStart Decision Control
SessionStart hooks allow you to load in context at the start of a session.
"hookSpecificOutput.additionalContext"adds the string to the context.
{
"hookSpecificOutput": {
"hookEventName": "SessionStart",
"additionalContext": "My additional context here"
}
}
Exit Code Example: Bash Command Validation
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import json
import re
import sys
# Define validation rules as a list of (regex pattern, message) tuples
VALIDATION_RULES = [
(
r"\bgrep\b(?!.*\|)",
"Use 'rg' (ripgrep) instead of 'grep' for better performance and features",
),
(
r"\bfind\s+\S+\s+-name\b",
"Use 'rg --files | rg pattern' or 'rg --files -g pattern' instead of 'find -name' for better performance",
),
]
def validate_command(command: str) -> list[str]:
issues = []
for pattern, message in VALIDATION_RULES:
if re.search(pattern, command):
issues.append(message)
return issues
try:
input_data = json.load(sys.stdin)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"Error: Invalid JSON input: {e}", file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(1)
tool_name = input_data.get("tool_name", "")
tool_input = input_data.get("tool_input", {})
command = tool_input.get("command", "")
if tool_name != "Bash" or not command:
sys.exit(1)
# Validate the command
issues = validate_command(command)
if issues:
for message in issues:
print(f"• {message}", file=sys.stderr)
# Exit code 2 blocks tool call and shows stderr to Claude
sys.exit(2)
JSON Output Example: UserPromptSubmit to Add Context and Validation
For `UserPromptSubmit` hooks, you can inject context using either method:- Exit code 0 with stdout: Claude sees the context (special case for
UserPromptSubmit) - JSON output: Provides more control over the behavior
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import json
import sys
import re
import datetime
# Load input from stdin
try:
input_data = json.load(sys.stdin)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"Error: Invalid JSON input: {e}", file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(1)
prompt = input_data.get("prompt", "")
# Check for sensitive patterns
sensitive_patterns = [
(r"(?i)\b(password|secret|key|token)\s*[:=]", "Prompt contains potential secrets"),
]
for pattern, message in sensitive_patterns:
if re.search(pattern, prompt):
# Use JSON output to block with a specific reason
output = {
"decision": "block",
"reason": f"Security policy violation: {message}. Please rephrase your request without sensitive information."
}
print(json.dumps(output))
sys.exit(0)
# Add current time to context
context = f"Current time: {datetime.datetime.now()}"
print(context)
"""
The following is also equivalent:
print(json.dumps({
"hookSpecificOutput": {
"hookEventName": "UserPromptSubmit",
"additionalContext": context,
},
}))
"""
# Allow the prompt to proceed with the additional context
sys.exit(0)
JSON Output Example: PreToolUse with Approval
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import json
import sys
# Load input from stdin
try:
input_data = json.load(sys.stdin)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"Error: Invalid JSON input: {e}", file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(1)
tool_name = input_data.get("tool_name", "")
tool_input = input_data.get("tool_input", {})
# Example: Auto-approve file reads for documentation files
if tool_name == "Read":
file_path = tool_input.get("file_path", "")
if file_path.endswith((".md", ".mdx", ".txt", ".json")):
# Use JSON output to auto-approve the tool call
output = {
"decision": "approve",
"reason": "Documentation file auto-approved",
"suppressOutput": True # Don't show in transcript mode
}
print(json.dumps(output))
sys.exit(0)
# For other cases, let the normal permission flow proceed
sys.exit(0)
Working with MCP Tools
Claude Code hooks work seamlessly with
Model Context Protocol (MCP) tools. When MCP servers
provide tools, they appear with a special naming pattern that you can match in
your hooks.
MCP Tool Naming
MCP tools follow the pattern mcp__<server>__<tool>, for example:
mcp__memory__create_entities- Memory server’s create entities toolmcp__filesystem__read_file- Filesystem server’s read file toolmcp__github__search_repositories- GitHub server’s search tool
Configuring Hooks for MCP Tools
You can target specific MCP tools or entire MCP servers:
{
"hooks": {
"PreToolUse": [
{
"matcher": "mcp__memory__.*",
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "echo 'Memory operation initiated' >> ~/mcp-operations.log"
}
]
},
{
"matcher": "mcp__.*__write.*",
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "/home/user/scripts/validate-mcp-write.py"
}
]
}
]
}
}
Examples
For practical examples including code formatting, notifications, and file protection, see [More Examples](/en/docs/claude-code/hooks-guide#more-examples) in the get started guide.Security Considerations
Disclaimer
USE AT YOUR OWN RISK: Claude Code hooks execute arbitrary shell commands on
your system automatically. By using hooks, you acknowledge that:
- You are solely responsible for the commands you configure
- Hooks can modify, delete, or access any files your user account can access
- Malicious or poorly written hooks can cause data loss or system damage
- Anthropic provides no warranty and assumes no liability for any damages
resulting from hook usage - You should thoroughly test hooks in a safe environment before production use
Always review and understand any hook commands before adding them to your
configuration.
##
Security Best Practices
Here are some key practices for writing more secure hooks:
- Validate and sanitize inputs - Never trust input data blindly
- Always quote shell variables - Use
"$VAR"not$VAR - Block path traversal - Check for
..in file paths - Use absolute paths - Specify full paths for scripts (use
$CLAUDE_PROJECT_DIRfor the project path) - Skip sensitive files - Avoid
.env,.git/, keys, etc.
Configuration Safety
Direct edits to hooks in settings files don’t take effect immediately. Claude
Code:
- Captures a snapshot of hooks at startup
- Uses this snapshot throughout the session
- Warns if hooks are modified externally
- Requires review in
/hooksmenu for changes to apply
This prevents malicious hook modifications from affecting your current session.
Hook Execution Details
- Timeout: 60-second execution limit by default, configurable per command.
- A timeout for an individual command does not affect the other commands.
- Parallelization: All matching hooks run in parallel
- Environment: Runs in current directory with Claude Code’s environment
- The
CLAUDE_PROJECT_DIRenvironment variable is available and contains the
absolute path to the project root directory
- The
- Input: JSON via stdin
- Output:
- PreToolUse/PostToolUse/Stop: Progress shown in transcript (Ctrl-R)
- Notification: Logged to debug only (
--debug)
Debugging
Basic Troubleshooting
If your hooks aren’t working:
- Check configuration - Run
/hooksto see if your hook is registered - Verify syntax - Ensure your JSON settings are valid
- Test commands - Run hook commands manually first
- Check permissions - Make sure scripts are executable
- Review logs - Use
claude --debugto see hook execution details
Common issues:
- Quotes not escaped - Use
\"inside JSON strings - Wrong matcher - Check tool names match exactly (case-sensitive)
- Command not found - Use full paths for scripts
Advanced Debugging
For complex hook issues:
- Inspect hook execution - Use
claude --debugto see detailed hook
execution - Validate JSON schemas - Test hook input/output with external tools
- Check environment variables - Verify Claude Code’s environment is correct
- Test edge cases - Try hooks with unusual file paths or inputs
- Monitor system resources - Check for resource exhaustion during hook
execution - Use structured logging - Implement logging in your hook scripts
Debug Output Example
Use claude --debug to see hook execution details:
[DEBUG] Executing hooks for PostToolUse:Write
[DEBUG] Getting matching hook commands for PostToolUse with query: Write
[DEBUG] Found 1 hook matchers in settings
[DEBUG] Matched 1 hooks for query "Write"
[DEBUG] Found 1 hook commands to execute
[DEBUG] Executing hook command: <Your command> with timeout 60000ms
[DEBUG] Hook command completed with status 0: <Your stdout>
Progress messages appear in transcript mode (Ctrl-R) showing:
- Which hook is running
- Command being executed
- Success/failure status
- Output or error messages
Security & Permissions
Tool Permission Patterns
# Allow specific tools (read/edit files)
claude --allowedTools "Edit,Read"
# Allow tool categories incl. Bash (but still scoped below)
claude --allowedTools "Edit,Read,Bash"
# Scoped permissions (all git commands)
claude --allowedTools "Bash(git:*)"
# Multiple scopes (git + npm)
claude --allowedTools "Bash(git:*),Bash(npm:*)"
Dangerous Mode
[!Warning]
NEVER use in Production systems, shared machines, or any systems with important data
Only use with isolated environments like a Docker container, using this mode can cause data loss and comprimise your system!
claude --dangerously-skip-permissions
Security Best Practices
Start Restrictive
Protect Sensitive Data
- Keep
~/.claude.jsonprivate (chmod 600). - Prefer environment variables for API keys over plain‑text.
- Use
--strict-mcp-configto only load MCP servers from specified config files
Automation & Integration
Automation & Scripting with Claude Code
GitHub Actions you can copy/paste :p
- Install the Claude GitHub App on your org/repo (required for Actions to comment on PRs/issues).
- In your repo, add a secret
ANTHROPIC_API_KEYSettings → Secrets and variables → Actions → New repository secret - Copy the workflows below into
.github/workflows/. - Open a test PR (or a new issue) to see them run.
[!TIP]
Pin Actions to a release tag (e.g.@v1) when you adopt them long‑term. The snippets below use branch tags for readability.
Auto PR Review (inline comments)
Creates a structured review (with inline comments) as soon as a PR opens or updates.
File: .github/workflows/claude-pr-auto-review.yml
name: Auto review PRs
on:
pull_request:
types: [opened, synchronize, reopened, ready_for_review]
permissions:
contents: read
pull-requests: write
jobs:
auto-review:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
fetch-depth: 1
- name: Claude PR review
uses: anthropics/claude-code-action@main
with:
anthropic_api_key: ${{ secrets.ANTHROPIC_API_KEY }}
# Claude will fetch the diff and leave inline comments
direct_prompt: |
Review this pull request’s diff for correctness, readability, testing, performance, and DX.
Prefer specific, actionable suggestions. Use inline comments where relevant.
# GitHub tools permitted during the run:
allowed_tools: >-
mcp__github__get_pull_request_diff,
mcp__github__create_pending_pull_request_review,
mcp__github__add_comment_to_pending_review,
mcp__github__submit_pending_pull_request_review
Security Review on Every PR
Runs a focused security scan and comments findings directly on the PR.
File: .github/workflows/claude-security-review.yml
name: Security Review
on:
pull_request:
permissions:
contents: read
pull-requests: write
jobs:
security:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
ref: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha || github.sha }}
fetch-depth: 2
- name: Claude Code Security Review
uses: anthropics/claude-code-security-review@main
with:
claude-api-key: ${{ secrets.ANTHROPIC_API_KEY }}
comment-pr: true
# Optional:
# exclude-directories: "docs,examples"
# claudecode-timeout: "20"
# claude-model: "claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620"
Issue Triage (suggest labels & severity)
When a new issue opens, Claude proposes labels/severity and posts a tidy triage comment. You can enable auto‑apply labels by flipping a single flag
File: .github/workflows/claude-issue-triage.yml
name: Claude Issue Triage
on:
issues:
types: [opened, edited, reopened]
permissions:
contents: read
issues: write
jobs:
triage:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
env:
CLAUDE_MODEL: claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620
steps:
- name: Collect context & similar issues
id: gather
env:
GH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
run: |
TITLE="${{ github.event.issue.title }}"
BODY="${{ github.event.issue.body }}"
# naive similar search by title words
Q=$(echo "$TITLE" | tr -dc '[:alnum:] ' | awk '{print $1" "$2" "$3" "$4}')
gh api -X GET search/issues -f q="repo:${{ github.repository }} is:issue $Q" -f per_page=5 > similars.json
echo "$TITLE" > title.txt
echo "$BODY" > body.txt
- name: Ask Claude for triage JSON
env:
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY: ${{ secrets.ANTHROPIC_API_KEY }}
run: |
cat > payload.json << 'JSON'
{
"model": "${{ env.CLAUDE_MODEL }}",
"max_tokens": 1500,
"system": "You are a pragmatic triage engineer. Be specific, cautious with duplicates.",
"messages": [{
"role": "user",
"content": [{
"type":"text",
"text":"Given the issue and similar candidates, produce STRICT JSON with keys: labels (array of strings), severity (one of: low, medium, high, critical), duplicate_url (string or empty), comment_markdown (string brief). Do not include any extra keys."
},
{"type":"text","text":"Issue title:\n"},
{"type":"text","text": (include from file) },
{"type":"text","text":"\n\nIssue body:\n"},
{"type":"text","text": (include from file) },
{"type":"text","text":"\n\nSimilar issues (JSON):\n"},
{"type":"text","text": (include from file) }]
}]
}
JSON
# Inject files safely
jq --arg title "$(cat title.txt)" '.messages[0].content[2].text = $title' payload.json \
| jq --arg body "$(cat body.txt)" '.messages[0].content[4].text = $body' \
| jq --arg sims "$(cat similars.json)" '.messages[0].content[6].text = $sims' > payload.final.json
curl -s https://api.anthropic.com/v1/messages \
-H "x-api-key: $ANTHROPIC_API_KEY" \
-H "anthropic-version: 2023-06-01" \
-H "content-type: application/json" \
-d @payload.final.json > out.json
jq -r '.content[0].text' out.json > triage.json || echo '{}' > triage.json
# Validate JSON to avoid posting garbage
jq -e . triage.json >/dev/null 2>&1 || echo '{"labels":[],"severity":"low","duplicate_url":"","comment_markdown":"(triage failed to parse)"}' > triage.json
- name: Apply labels (optional)
if: ${{ false }} # flip to `true` to auto-apply labels
uses: actions/github-script@v7
with:
script: |
const triage = JSON.parse(require('fs').readFileSync('triage.json','utf8'))
if (triage.labels?.length) {
await github.rest.issues.addLabels({
owner: context.repo.owner,
repo: context.repo.repo,
issue_number: context.issue.number,
labels: triage.labels
})
}
- name: Post triage comment
uses: actions/github-script@v7
with:
script: |
const fs = require('fs')
const triage = JSON.parse(fs.readFileSync('triage.json','utf8'))
const md = `### 🤖 Triage
- **Suggested labels:** ${triage.labels?.join(', ') || '—'}
- **Severity:** ${triage.severity || '—'}
${triage.duplicate_url ? `- **Possible duplicate:** ${triage.duplicate_url}\n` : ''}
---
${triage.comment_markdown || ''}`
await github.rest.issues.createComment({
owner: context.repo.owner,
repo: context.repo.repo,
issue_number: context.issue.number,
body: md
})
[!NOTE]
The triage workflow posts a suggestion comment by default. Flip theApply labelsstep totrueif you want labels applied automatically.Configuration & Customization
- Model selection: set
CLAUDE_MODEL(e.g.,claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620) where shown.- Secrets:
ANTHROPIC_API_KEYis required. The built‑inGITHUB_TOKENis sufficient for posting comments and applying labels.- Permissions: each workflow declares the least privileges it needs (
pull-requests: writeand/orissues: write). Adjust only if your org requires stricter policies.- Scope: use
paths:filters on triggers to limit when workflows run (e.g., only for/srcor exclude/docs).Troubleshooting
Check the Actions logs first—most issues are missing secrets/permissions or a mis‑indented YAML block.
- No comments appear on PRs: Verify the Claude GitHub App is installed and the workflow has
pull-requests: writepermission.- 403 when applying labels: Ensure the job or step has
issues: write. The defaultGITHUB_TOKENmust have access to this repo.- Anthropic API errors: Confirm
ANTHROPIC_API_KEYis set at repository (or org) level and not expired.- “YAML not well‑formed”: Validate spacing—two spaces per nesting level; no tabs.
Help & Troubleshooting
[!TIP]
Q:claudenot found, butnpx claudeworks?A: Your
PATHis missing the npm global bin. See thePATHissue section forWindowsorLinuxQ: Which Node.js version do I need?
A: Node.js 18+ (ideally 20+). Check with
node --version.Q: Where do I see logs
A: Run
claude doctorandclaude --verbosethe diagnostic window will point to log locations.Q: Do I need to reboot after editing PATH?
A: No reboot required, but you must open a new terminal window.
Debug Quick Commands
Check the output of claude doctor for log locations and environment checks.
[!Note]
claude # Open Claude UI (if on PATH) claude --version # Show CLI version (e.g., 1.0.xx) claude update # Update the CLI (if supported) claude doctor # Open diagnostic / debug window npx claude /doctor # Opens diagnostic/debug window claude --debug # Launch claude with diagnostics claude --verbose # Verbose logging where claude # Windows (cmd) which claude # macOS/Linux (bash/zsh) npm bin -g # Linux Verify your global bin path npm prefix -g # Windows Verify your global bin path
Path Temp Fix
Your PATH likely doesn’t include the global npm bin directory.
[!Note]
Windows (CMD):
set PATH=%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\npm;C:\Program Files\nodejs;%PATH% where claude claude --debuggWindows (PowerShell):
$env:Path = "$env:USERPROFILE\AppData\Roaming\npm;C:\Program Files\nodejs;$env:Path" where claude claude --debuggLinux/MacOS (bash/zsh)
export PATH="$(npm config get prefix)/bin:$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH" which claude claude doctor
Windows Path Perm Fix
Replace <you> with your own Windows username (without the angle brackets)
- Start → type: Environment Variables
- Open Edit the system environment variables → Environment Variables
- Under User variables for select
Path→Edit→Newadd:
C:\Users\<you>\AppData\Roaming\npm
C:\Program Files\nodejs</kbd>
Optional locations to add:
C:\Users\<you>\.claude\local\bin
C:\Users\<you>\.local\bin
- Remove duplicates, any entry containing
%PATH%, and stray quotes ("). ClickOK. - Open a
newCommand Prompt/PowerShell and verify:
where claude
claude doctor
[!Tip]
Optional Run directly (when PATH is broken)
Windows (PowerShell/cmd)
"%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\npm\claude.cmd" --version "%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\npm\claude.cmd" doctorOr via npx:
npx claude doctor
Installation / Node.js Issues
Must be Node 18+ (20+ recommended)
node --version
Clean uninstall
npm uninstall -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
Fresh install
npm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
Authentication Issues
> *Verify your Anthropic API key is available to the CLI.*PowerShell (Windows):
echo $env:ANTHROPIC_API_KEY
claude -p "test" --verbose
bash/zsh (macOS/Linux):
echo $ANTHROPIC_API_KEY
claude -p "test" --verbose
If the variable is empty set it for your shell/profile or use your OS keychain/secrets manager.
Permission / Allowed Tools Issues
Inspect permissions
claude config get allowedTools
Reset permissions
claude config set allowedTools "[]"
Minimal safe set (example)
claude config set allowedTools '["Edit","View"]'
MCP (Model Context Protocol) Issues
Debug MCP servers
claude --mcp-debug
List & remove MCP servers
claude mcp list
claude mcp remove <server-name>
Full Clean Reinstall (Windows / PowerShell)
[!Caution]
The following removes Claude Code binaries, caches, and config under your user profile
- Uninstall the global npm package
npm uninstall -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
- Remove leftover shim files
Remove-Item -LiteralPath "$env:USERPROFILE\AppData\Roaming\npm\claude*" -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Remove-Item -LiteralPath "$env:USERPROFILE\AppData\Roaming\npm\node_modules\@anthropic-ai\claude-code" -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
- Delete cached installer & native files
Remove-Item -LiteralPath "$env:USERPROFILE\.claude\downloads\*" -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Remove-Item -LiteralPath "$env:USERPROFILE\.claude\local\bin\claude.exe" -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Remove-Item -LiteralPath "$env:USERPROFILE\.claude\local" -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
- Remove config and project-local files
Remove-Item -LiteralPath "$env:USERPROFILE\.claude.json" -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Remove-Item -LiteralPath "$env:USERPROFILE\.claude" -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
- Reinstall
npm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
One‑Shot Health Check (copy/paste)
Windows (PowerShell):
Write-Host "`n=== Node & npm ==="; node --version; npm --version
Write-Host "`n=== Where is claude? ==="; where claude
Write-Host "`n=== Try doctor ==="; try { claude doctor } catch { Write-Host "claude not on PATH" }
Write-Host "`n=== API key set? ==="; if ($env:ANTHROPIC_API_KEY) { "Yes" } else { "No" }
macOS/Linux (bash/zsh):
echo "=== Node & npm ==="; node --version; npm --version
echo "=== Where is claude? ==="; which claude || echo "claude not on PATH"
echo "=== Try doctor ==="; claude doctor || true
echo "=== API key set? ==="; [ -n "$ANTHROPIC_API_KEY" ] && echo Yes || echo No
Appendix: Useful Paths
- Windows npm global bin:
C:\Users\<you>\AppData\Roaming\npm - Windows Node.js:
C:\Program Files\nodejs - Claude local data (Win):
C:\Users\<you>\.claude\ - Claude config (Win):
C:\Users\<you>\.claude.json - macOS/Linux npm global bin:
$(npm config get prefix)/bin(often/usr/local/binor$HOME/.npm-global/bin)
Best Practices
Curated guidance for safe, fast, and correct use of the Claude Code CLI and interactive REPL. All commands and flags here match the current Anthropic docs as of Aug 23, 2025.
Effective Prompting
# Good: Specific and detailed
claude "Review UserAuth.js for security vulnerabilities, focusing on JWT handling"
# Bad: Vague
claude "check my code"
Tip: claude "query" starts the interactive REPL pre-seeded with your prompt; claude -p "query" runs print mode (non‑interactive) and exits.
Security Best Practices
-
Start with minimal permissions
- Prefer explicit allows and denies, either on the CLI or in settings files.
# Allow only what you need for this run claude --allowedTools "Read" "Grep" "LS" "Bash(npm run test:*)"Or commit a project policy at
.claude/settings.json:{ "permissions": { "allow": ["Read", "Grep", "LS", "Bash(npm run test:*)"], "deny": ["WebFetch", "Bash(curl:*)", "Read(./.env)", "Read(./secrets/**)"] } } -
Handle secrets correctly
- Use environment variables for SDK/automation flows:
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="your_key" # for SDK/print mode- In the interactive REPL, prefer
/logininstead of hard‑coding tokens. - Deny access to sensitive files in settings (replaces older
ignorePatterns):
{ "permissions": { "deny": ["Read(./.env)", "Read(./.env.*)", "Read(./secrets/**)"] } } -
Audit permissions regularly
# Project settings claude config list claude config get permissions.allow claude config get permissions.deny # Global settings claude config list -g -
Avoid bypass modes in production
- Do not use
--dangerously-skip-permissionsoutside isolated/dev sandboxes. - For unattended runs, combine narrow
--allowedToolswith--disallowedToolsand project settings.
- Do not use
Performance Tips
-
Use machine‑readable output in automations
claude -p "summarize this error log" --output-format json # valid: text | json | stream-json -
Bound non‑interactive work
claude -p "run type checks and summarize failures" --max-turns 3 # optionally also bound thinking: export MAX_THINKING_TOKENS=20000 -
Keep sessions tidy
# Retain recent sessions only (default is 30 days) claude config set -g cleanupPeriodDays 20 -
Limit context scope
# Grant access only to relevant paths to reduce scanning/noise claude --add-dir ./services/api ./packages/ui -
Pick the right model
- CLI aliases:
--model sonnetor--model opus(latest of that family). - For reproducibility in settings, pin a full model ID (e.g.,
"claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022").
- CLI aliases:
Monitoring & Alerting
1) Health checks
Use the built‑in doctor command to verify installation and environment.
# Every 15 minutes
*/15 * * * * /usr/local/bin/claude doctor >/dev/null 2>&1 || \
mail -s "Claude Code doctor failed" admin@company.com </dev/null
2) Log analysis batch job
# Daily analysis with non-interactive JSON output (print mode)
0 6 * * * tail -1000 /var/log/app.log | \
claude -p "Analyze errors, regressions, and suspect patterns; output JSON." \
--output-format json > /tmp/daily-analysis.json
3) Telemetry (optional)
Claude Code emits OpenTelemetry metrics/events. Set exporters in settings/env (e.g., OTLP) and ship to your observability stack (Datadog, Honeycomb, Prometheus/Grafana, etc.).
Collaboration Best Practices
Team Workflows
1) Share versioned configuration
// .claude/settings.json (checked into the repo)
{
"permissions": {
"allow": ["Read", "Grep", "LS", "Bash(npm run lint)", "Bash(npm run test:*)"],
"deny": ["WebFetch", "Read(./.env)", "Read(./.env.*)", "Read(./secrets/**)"]
},
// Pin a model here for reproducibility if desired, using a full model ID:
"model": "claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022"
}
2) Documentation automation
# Update docs with explicit tasks
claude "Update README.md to reflect the latest API endpoints and examples."
claude "Generate TypeScript types from schema.prisma and write to /types."
3) Code review standards
# Review a local diff with constrained tools
git fetch origin main
git diff origin/main...HEAD > /tmp/diff.patch
claude --allowedTools "Read" "Grep" "Bash(git:*)" \
"Review /tmp/diff.patch using team standards:
- Security best practices
- Performance considerations
- Code style compliance
- Test coverage adequacy"
Knowledge Sharing
1) Project runbooks
claude "Create a deployment runbook for this app: steps, checks, rollback."
claude "Document onboarding for new developers: setup, commands, conventions."
2) Architecture docs
claude "Update architecture docs to reflect new microservices."
claude "Create sequence diagrams for the authentication flow."
Tip: Keep durable context in CLAUDE.md at the project root. In the REPL, use
/memoryto manage it and@pathto import file content into prompts.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Security
❌ Don’t
- Use
--dangerously-skip-permissionson production systems - Hard‑code secrets in commands/config
- Grant overly broad permissions (e.g.,
Bash(*)) - Run with elevated privileges unnecessarily
✅ Do
- Store secrets in env vars and credential helpers
- Start from minimal
permissions.allowand expand gradually - Audit with
claude config list/claude config get - Isolate risky operations in containers/VMs
Performance
❌ Don’t
- Load an entire monorepo when you only need a package
- Max out thinking/turn budgets for simple tasks
- Ignore session cleanup
✅ Do
- Use
--add-dirfor focused context - Right‑size with
--max-turnsandMAX_THINKING_TOKENS - Set
cleanupPeriodDaysto prune old sessions
Workflow
❌ Don’t
- Skip project context (
CLAUDE.md) - Use vague prompts
- Ignore errors/logs
- Automate without testing
✅ Do
- Maintain and update
CLAUDE.md - Be specific and goal‑oriented in prompts
- Monitor via logs/OTel as appropriate
- Test automation in safe environments first
Third-Party Integrations
DeepSeek Integration
npm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
export ANTHROPIC_BASE_URL=https://api.deepseek.com/anthropic
export ANTHROPIC_AUTH_TOKEN=${YOUR_API_KEY}
export ANTHROPIC_MODEL=deepseek-chat
export ANTHROPIC_SMALL_FAST_MODEL=deepseek-chat
Find more information from the Official Deepseek Docs
总结
恭喜您完成了这份《Claude Code 指南》的学习。通过本指南,您已经全面了解了如何从零开始安装、配置并在各种场景下高效使用 Claude Code 这一前沿的 AI 编程工具。 我们共同探索了其丰富的功能,从基本的代码问答、文件编辑,到如自动化代码审查、安全漏洞扫描等高级的自动化与集成能力。更重要的是,您掌握了如何通过环境变量、配置文件、子代理以及强大的钩子系统(Hooks System)来深度定制 Claude Code,使其完美契合您的个人偏好与团队规范。 请牢记,Claude Code 不仅仅是一个工具,更是一位能够深度理解项目上下文、与您在终端里并肩作战的开发伙伴。将本指南中学到的知识应用到您的日常工作中,不断实践与探索,您将发现它在提升代码质量、加速开发周期和简化复杂任务方面带来的巨大价值。随着技术的不断演进,我们鼓励您保持好奇心,继续探索 AI 在软件开发领域的无限可能。更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)