AI工具在现代软件开发与人工智能项目中的应用
GitHub Copilot 是由 GitHub 与 OpenAI 联合开发的一款基于大型语言模型(LLM)的AI编程助手。它通过分析上下文(如函数名、注释、已有代码等),自动生成代码建议,支持多种编程语言,包括 Python、JavaScript、Java、C++、Go 等。其底层模型为 Codex,是 GPT-3 的一个变种,专门针对代码生成任务进行训练,能够在开发者编写代码时提供实时补全建议
随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,AI工具已经成为现代软件开发、数据科学和机器学习项目中不可或缺的一部分。这些工具不仅提升了开发效率,还显著降低了技术门槛,使得更多开发者能够快速构建高质量的应用程序。本文将深入探讨三类核心AI工具:智能编码辅助工具(如GitHub Copilot)、数据标注工具 和 模型训练平台,结合实际代码示例、流程图(使用Mermaid语法)、Prompt设计案例以及图表分析,全面展示它们在真实场景中的集成方式与价值。
一、智能编码辅助工具:GitHub Copilot
1.1 简介
GitHub Copilot 是由 GitHub 与 OpenAI 联合开发的一款基于大型语言模型(LLM)的AI编程助手。它通过分析上下文(如函数名、注释、已有代码等),自动生成代码建议,支持多种编程语言,包括 Python、JavaScript、Java、C++、Go 等。
其底层模型为 Codex,是 GPT-3 的一个变种,专门针对代码生成任务进行训练,能够在开发者编写代码时提供实时补全建议。
1.2 工作原理
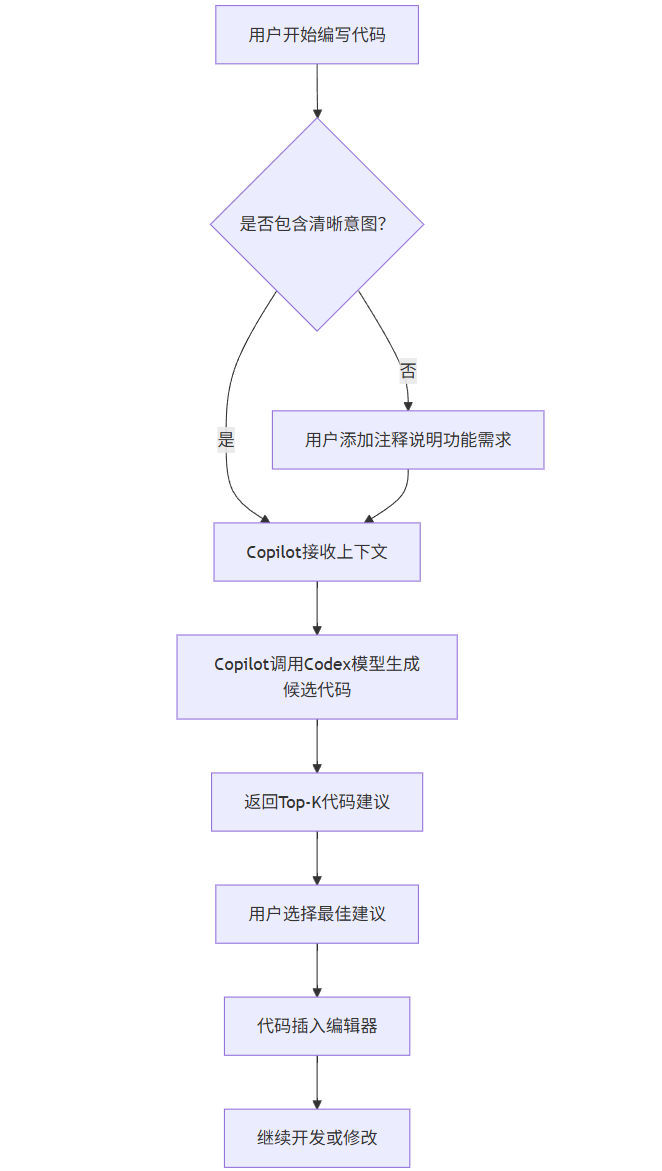
GitHub Copilot 在用户输入部分代码或注释后,会向云端服务器发送当前编辑器上下文,服务器返回多个可能的代码片段供选择。整个过程类似于“智能自动补全”,但远比传统IDE的补全功能强大。
Mermaid 流程图:GitHub Copilot 工作流程
1.3 实际代码示例
假设我们要实现一个简单的 Python 函数来计算斐波那契数列第 n 项。
手动编写方式:
python
def fibonacci(n):
if n <= 0:
return 0
elif n == 1:
return 1
else:
a, b = 0, 1
for _ in range(2, n + 1):
a, b = b, a + b
return b
print(fibonacci(10)) # 输出: 55
使用 GitHub Copilot 的方式:
只需输入以下注释,Copilot 即可自动生成完整函数:
python
# Function to compute the nth Fibonacci number using iterative approach
def fibonacci(n):
此时,Copilot 会在下一行自动提示:
python
if n <= 0:
return 0
elif n == 1:
return 1
else:
a, b = 0, 1
for i in range(2, n + 1):
a, b = b, a + b
return b
这大大减少了手动编写时间,并减少了出错概率。
1.4 Prompt 设计技巧(用于引导 Copilot)
虽然 Copilot 主要依赖上下文,但良好的注释可以显著提升生成质量。以下是几种有效的 Prompt 模式:
|
功能描述 |
|
|
输入输出说明 |
|
|
错误修复提示 |
|
|
架构建议 |
|
例如:
python
# Write a function that takes a list of integers and returns only even numbers greater than 10
def filter_even_gt_10(nums):
Copilot 可能生成:
return [x for x in nums if x > 10 and x % 2 == 0]
1.5 优势与挑战
|
提高编码速度(平均提升 30%-50%) |
可能生成不安全或存在漏洞的代码 |
|
支持多语言 |
对复杂业务逻辑理解有限 |
|
减少重复性劳动 |
需要人工审查与测试 |
|
帮助初学者学习语法 |
存在版权争议(训练数据来源) |
二、数据标注工具:Label Studio 与 CVAT
2.1 数据标注的重要性
在机器学习项目中,尤其是监督学习,高质量的标注数据是模型性能的关键。无论是图像分类、目标检测、语义分割还是文本情感分析,都需要经过人工或半自动方式打标签的数据集。
然而,手动标注耗时且成本高昂。因此,专业的数据标注工具应运而生。
2.2 常见工具对比
|
Label Studio |
多模态 |
图像、文本、音频、视频 |
✅ |
界面友好,支持规则引擎 |
|
CVAT (Computer Vision Annotation Tool) |
图像/视频 |
JPEG, PNG, MP4, AVI |
✅ |
强大的视频标注能力 |
|
Supervisely |
图像/点云 |
多种格式 |
❌(商业版为主) |
集成训练 pipeline |
|
Amazon SageMaker Ground Truth |
全托管服务 |
所有主流格式 |
❌ |
支持众包标注 |
我们以 Label Studio 为例进行详细讲解。
2.3 Label Studio 使用流程
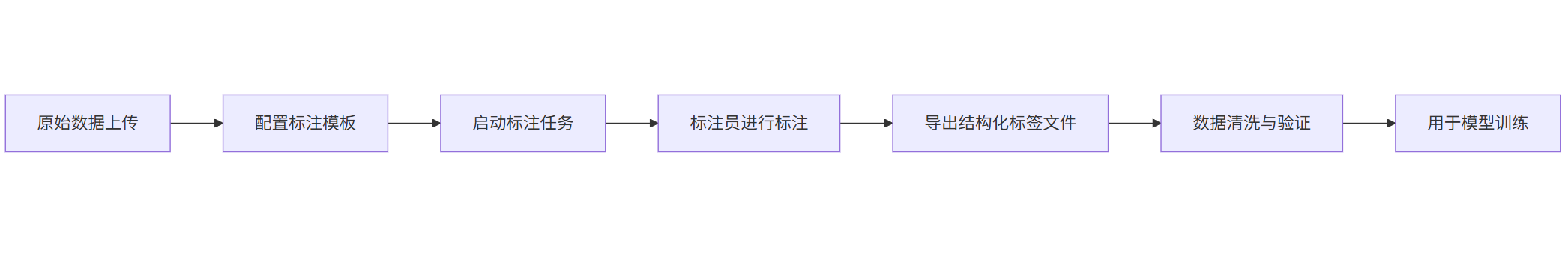
Mermaid 流程图:数据标注流程
graph LR
A[原始数据上传] --> B[配置标注模板]
B --> C[启动标注任务]
C --> D[标注员进行标注]
D --> E[导出结构化标签文件]
E --> F[数据清洗与验证]
F --> G[用于模型训练]
2.4 标注模板配置(XML/JSON)
Label Studio 使用 JSON 或 XML 定义标注界面。以下是一个图像分类任务的配置示例:
xml
<View>
<Image name="image" value="$image_url"/>
<Choices name="label" toName="image">
<Choice value="Cat"/>
<Choice value="Dog"/>
<Choice value="Other"/>
</Choices>
</View>
对于更复杂的任务,如目标检测:
xml
<View>
<Image name="img" value="$image_url"/>
<RectangleLabels name="rect" toName="img">
<Label value="Person"/>
<Label value="Car"/>
<Label value="Tree"/>
</RectangleLabels>
</View>
2.5 实际操作步骤(命令行+Web界面)
bash
# 安装 Label Studio
pip install label-studio
# 启动服务
label-studio start my_project --port 8080
打开浏览器访问 http://localhost:8080,导入图片目录,选择上述模板,即可开始标注。
标注完成后,导出为 COCO 格式或 JSON:
json
[
{
"id": 1,
"data": {"image": "https://example.com/images/cat1.jpg"},
"annotations": [
{
"result": [
{
"value": {"choices": ["Cat"]},
"type": "choices"
}
]
}
]
}
]
2.6 自动预标注(AI 辅助标注)
Label Studio 支持连接预训练模型进行自动标注,大幅减少人工工作量。
例如,使用 YOLOv8 检测模型作为 backend:
python
from ultralytics import YOLO
import cv2
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
def predict_bboxes(image_path):
results = model(image_path)
boxes = results[0].boxes.xyxy.cpu().numpy()
classes = results[0].boxes.cls.cpu().numpy()
return [{"x": box[0], "y": box[1], "width": box[2]-box[0], "height": box[3]-box[1], "label": int(cls)}
for box, cls in zip(boxes, classes)]
然后通过 Label Studio 的 ML Backend 集成该 API,实现“智能初标 + 人工校正”模式。
2.7 效率提升分析图表
pie
title 数据标注方式效率对比(单位:小时/千张图)
“纯人工标注” : 40
“AI初标 + 人工修正” : 12
“全自动(无验证)” : 2
可见,结合AI辅助后,效率提升超过 70%。
三、模型训练平台:Hugging Face + Google Colab + AWS SageMaker
3.1 平台概览
|
Hugging Face |
开源模型库 |
NLP为主 |
✅ |
模型即服务,社区活跃 |
|
Google Colab |
Jupyter环境 |
教学/轻量训练 |
✅(有限GPU) |
易上手,集成Python |
|
AWS SageMaker |
企业级平台 |
大规模生产部署 |
❌(按量计费) |
全生命周期管理 |
|
Azure ML |
微软生态 |
企业AI工程化 |
❌ |
与Power BI等集成好 |
|
Alibaba PAI |
国内平台 |
中文NLP、推荐系统 |
❌ |
支持MaxCompute对接 |
我们将重点介绍 Hugging Face + Colab 的组合,适合大多数中小型项目。
3.2 Hugging Face 快速入门
Hugging Face 提供了 transformers 库,封装了数千个预训练模型(BERT、GPT、T5、ViT等),并支持微调(Fine-tuning)。
示例:文本分类任务(情感分析)
Step 1: 安装依赖
bash
pip install transformers datasets torch pandas scikit-learn
Step 2: 加载数据集
python
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("imdb")
train_data = dataset["train"].shuffle(seed=42).select(range(1000)) # 小样本演示
test_data = dataset["test"].select(range(100))
Step 3: 文本编码
python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
def tokenize_function(examples):
return tokenizer(examples["text"], truncation=True, padding="max_length", max_length=512)
tokenized_train = train_data.map(tokenize_function, batched=True)
tokenized_test = test_data.map(tokenize_function, batched=True)
Step 4: 训练模型
python
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification, TrainingArguments, Trainer
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased", num_labels=2)
def compute_metrics(eval_pred):
predictions, labels = eval_pred
predictions = np.argmax(predictions, axis=1)
return {"accuracy": accuracy_score(labels, predictions)}
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir="./results",
evaluation_strategy="epoch",
per_device_train_batch_size=8,
per_device_eval_batch_size=8,
num_train_epochs=3,
weight_decay=0.01,
logging_dir="./logs",
)
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=tokenized_train,
eval_dataset=tokenized_test,
compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
)
trainer.train()
Step 5: 推理预测
text = "This movie was absolutely fantastic!"
inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt", truncation=True, padding=True, max_length=512)
outputs = model(**inputs)
predictions = torch.nn.functional.softmax(outputs.logits, dim=-1)
print(predictions.detach().numpy()) # [0.02, 0.98] → 正面情绪
3.3 结合 Google Colab 的完整流程
Google Colab 提供免费 GPU(Tesla T4/K80),非常适合运行上述代码。
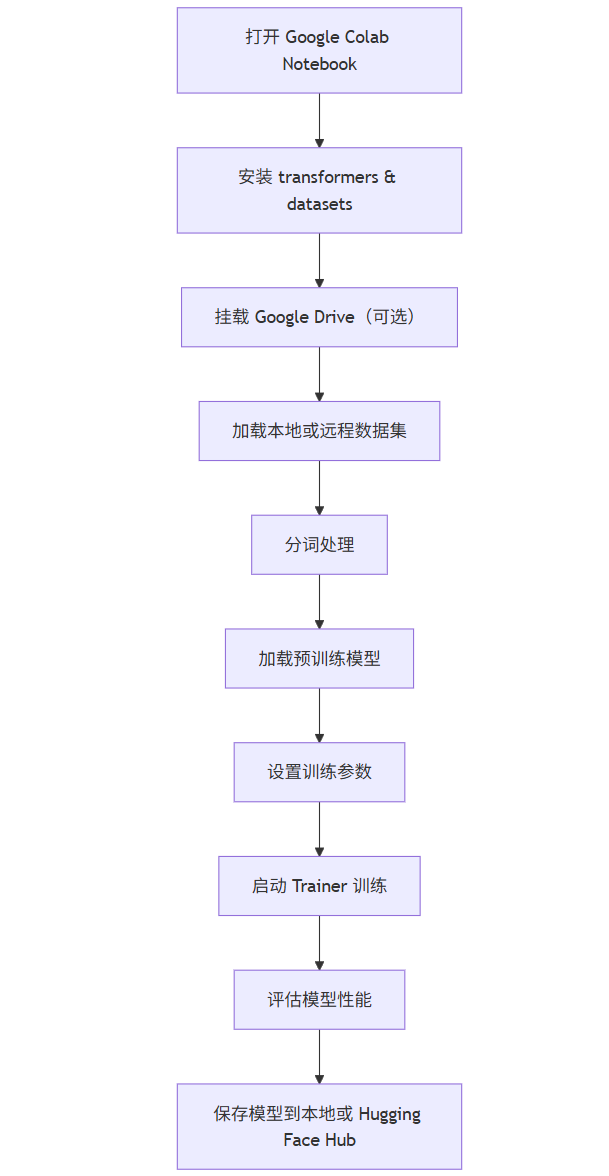
Mermaid 流程图:Colab + Hugging Face 训练流程
graph TB
A[打开 Google Colab Notebook] --> B[安装 transformers & datasets]
B --> C[挂载 Google Drive(可选)]
C --> D[加载本地或远程数据集]
D --> E[分词处理]
E --> F[加载预训练模型]
F --> G[设置训练参数]
G --> H[启动 Trainer 训练]
H --> I[评估模型性能]
I --> J[保存模型到本地或 Hugging Face Hub]
如何上传模型到 Hugging Face Hub?
python
# 登录 HF
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
notebook_login()
# 推送模型
model.push_to_hub("my-imdb-sentiment-model")
tokenizer.push_to_hub("my-imdb-sentiment-model")
3.4 企业级平台:AWS SageMaker 示例
对于需要大规模训练的企业场景,SageMaker 提供端到端解决方案。
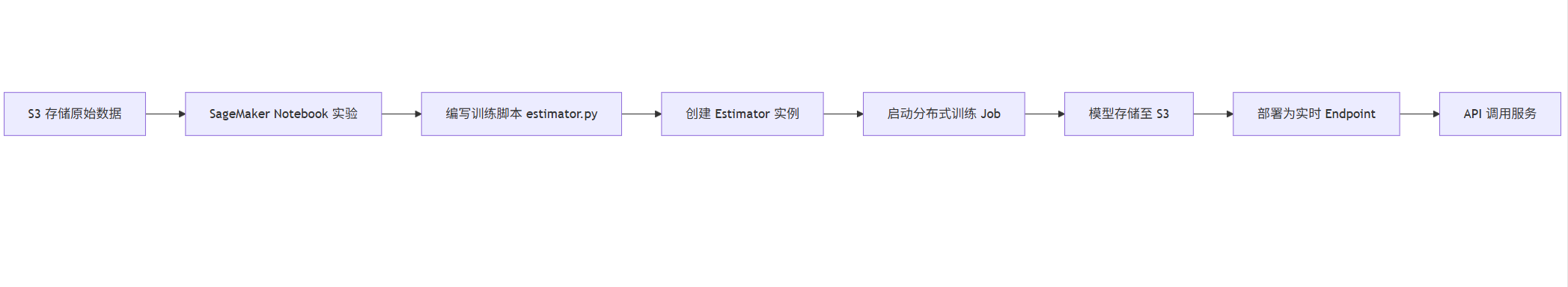
流程图:SageMaker 模型训练流程
graph LR
A[S3 存储原始数据] --> B[SageMaker Notebook 实验]
B --> C[编写训练脚本 estimator.py]
C --> D[创建 Estimator 实例]
D --> E[启动分布式训练 Job]
E --> F[模型存储至 S3]
F --> G[部署为实时 Endpoint]
G --> H[API 调用服务]
示例代码片段(estimator.py)
python
# estimator.py
import torch
import argparse
def train(model, train_loader, epochs):
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters())
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
for epoch in range(epochs):
for batch in train_loader:
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(batch['input_ids'])
loss = criterion(outputs, batch['labels'])
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
创建 Estimator 并启动训练
python
from sagemaker.huggingface import HuggingFace
hyperparameters = {
'epochs': 3,
'train_batch_size': 32,
'model_name': 'distilbert-base-uncased'
}
huggingface_estimator = HuggingFace(
entry_point='estimator.py',
source_dir='./scripts',
instance_type='ml.p3.2xlarge',
instance_count=1,
role=sagemaker_role,
transformers_version='4.26',
pytorch_version='1.13',
py_version='py39',
hyperparameters=hyperparameters
)
huggingface_estimator.fit({'train': 's3://my-bucket/train/', 'test': 's3://my-bucket/test/'})
四、三大工具协同工作的完整项目案例
4.1 项目背景:构建一个“社交媒体图片内容审核系统”
目标:自动识别社交平台上传的图片是否包含暴力内容。
4.2 技术栈整合
- 智能编码:GitHub Copilot 辅助编写数据处理与模型训练代码
- 数据标注:Label Studio 进行图像暴力内容标注(Yes/No)
- 模型训练:Hugging Face ViT 模型 + Colab 训练
- 部署:Flask API + Ngrok 外网访问
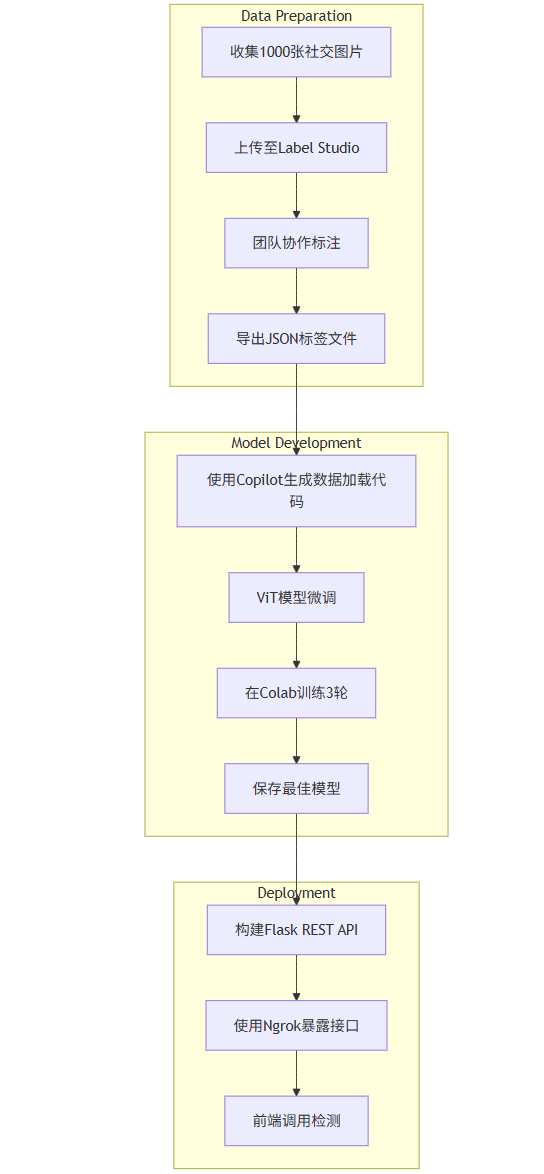
4.3 整体架构图(Mermaid)
graph TD
subgraph Data Preparation
A[收集1000张社交图片] --> B[上传至Label Studio]
B --> C[团队协作标注]
C --> D[导出JSON标签文件]
end
subgraph Model Development
D --> E[使用Copilot生成数据加载代码]
E --> F[ViT模型微调]
F --> G[在Colab训练3轮]
G --> H[保存最佳模型]
end
subgraph Deployment
H --> I[构建Flask REST API]
I --> J[使用Ngrok暴露接口]
J --> K[前端调用检测]
end
4.4 关键代码节选
数据加载(借助 Copilot 生成)
python
# Prompt: Load images and labels from Label Studio export for binary classification
import json
from PIL import Image
import os
with open('export.json') as f:
data = json.load(f)
images, labels = [], []
for item in data:
img_path = item['data']['image'].replace('http://localhost:8080', '/data')
label = 1 if "Violence" in item['annotations'][0]['result'][0]['value']['choices'] else 0
images.append(Image.open(img_path).convert("RGB"))
labels.append(label)
ViT 微调(Hugging Face)
from transformers import ViTFeatureExtractor, ViTForImageClassification
feature_extractor = ViTFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained('google/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k')
model = ViTForImageClassification.from_pretrained(
'google/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k',
num_labels=2,
id2label={0: "Safe", 1: "Violent"},
label2id={"Safe": 0, "Violent": 1}
)
Flask API 部署
python
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from torchvision import transforms
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/predict', methods=['POST'])
def predict():
file = request.files['image']
image = Image.open(file.stream).convert("RGB")
inputs = feature_extractor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(**inputs).logits
predicted_class = logits.argmax(-1).item()
confidence = torch.softmax(logits, dim=1)[0][predicted_class].item()
return jsonify({"class": model.config.id2label[predicted_class], "confidence": confidence})
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(port=5000)
运行后使用 ngrok http 5000 获取公网地址。
五、总结与趋势展望
5.1 三大工具的核心价值
|
智能编码工具 |
编码自动化,降低认知负荷 |
30%-50% |
|
数据标注工具 |
提升标注效率与一致性 |
60%-80% |
|
模型训练平台 |
快速实验迭代,简化部署 |
50%-70% |
5.2 当前局限性
- GitHub Copilot:仍需人工审查,不适合关键系统。
- 数据标注工具:自动标注精度依赖预模型质量。
- 训练平台:云成本高,冷启动慢。
5.3 未来发展趋势
- 多模态AI助手:下一代 Copilot 将支持代码+文档+图表联合生成。
- 主动学习标注系统:系统自动挑选最难样本优先标注,提升数据效率。
- AutoML 集成平台:从数据到模型一键生成,无需写代码。
- 边缘设备训练支持:手机端微调个性化模型成为可能。
六、参考资料与扩展阅读
- GitHub Copilot Documentation
- Label Studio 官方文档
- Hugging Face Transformers Docs
- AWS SageMaker Developer Guide
- Chen et al., "Evaluating Large Language Models for Code Generation", arXiv:2205.12664, 2022.
- Ramesh et al., "Zero-Shot Text-to-Image Generation using Diffusion Models", Nature, 2022.
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献43条内容
已为社区贡献43条内容







所有评论(0)