AI编程:自动化代码生成、低代码/无代码开发与算法优化实践
本文探讨了AI编程技术在软件开发中的关键应用,主要包括三大领域:1)自动化代码生成,通过AI模型和模板技术实现代码补全与优化;2)低代码/无代码开发平台,提供可视化界面构建应用程序;3)算法自动化优化,包括机器学习模型选择与深度学习调优。文章详细介绍了各项技术的实现方法,如基于OpenAI的代码生成、CRUD模板系统、AutoML流水线等,并提供了完整的代码示例。同时分析了AI编程的未来趋势,包括
1. 自动化代码生成
1.1 自动化代码生成概述
自动化代码生成是指利用人工智能技术自动生成、补全或优化代码的过程。这项技术正在彻底改变软件开发的方式,提高开发效率,减少重复性工作,并降低人为错误。
python
# 示例:使用OpenAI API进行代码生成
import openai
import json
class CodeGenerator:
def __init__(self, api_key):
openai.api_key = api_key
def generate_function(self, description, language="python"):
"""根据描述生成函数代码"""
prompt = f"""
请用{language}编写一个函数,实现以下功能:
{description}
要求:
1. 包含完整的函数定义
2. 添加适当的注释
3. 包含异常处理
4. 返回完整的可执行代码
"""
response = openai.Completion.create(
engine="text-davinci-003",
prompt=prompt,
max_tokens=1000,
n=1,
stop=None,
temperature=0.7
)
return response.choices[0].text.strip()
def code_completion(self, partial_code, language="python"):
"""代码补全"""
prompt = f"""
请补全以下{language}代码:
{partial_code}
只返回补全的代码部分,不要解释。
"""
response = openai.Completion.create(
engine="code-davinci-002",
prompt=prompt,
max_tokens=500,
n=1,
stop=None,
temperature=0.5
)
return response.choices[0].text.strip()
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 注意:需要有效的OpenAI API密钥
# generator = CodeGenerator("your-api-key")
# 生成排序函数
description = "实现一个快速排序算法,对整数列表进行升序排序"
# generated_code = generator.generate_function(description)
# print(generated_code)
1.2 自动化代码生成的技术实现
python
# 示例:基于模板的代码生成系统
class TemplateBasedGenerator:
def __init__(self):
self.templates = self.load_templates()
def load_templates(self):
"""加载代码模板"""
return {
"crud_controller": """
class {model_name}Controller:
def __init__(self):
self.service = {model_name}Service()
def create(self, data):
\"\"\"创建新的{model_name}记录\"\"\"
try:
result = self.service.create(data)
return {{"success": True, "data": result, "message": "创建成功"}}
except Exception as e:
return {{"success": False, "message": str(e)}}
def get_by_id(self, id):
\"\"\"根据ID获取{model_name}记录\"\"\"
try:
result = self.service.get_by_id(id)
if result:
return {{"success": True, "data": result}}
else:
return {{"success": False, "message": "记录不存在"}}
except Exception as e:
return {{"success": False, "message": str(e)}}
def update(self, id, data):
\"\"\"更新{model_name}记录\"\"\"
try:
result = self.service.update(id, data)
return {{"success": True, "data": result, "message": "更新成功"}}
except Exception as e:
return {{"success": False, "message": str(e)}}
def delete(self, id):
\"\"\"删除{model_name}记录\"\"\"
try:
self.service.delete(id)
return {{"success": True, "message": "删除成功"}}
except Exception as e:
return {{"success": False, "message": str(e)}}
def list_all(self, page=1, size=10):
\"\"\"获取{model_name}列表\"\"\"
try:
result = self.service.list_all(page, size)
return {{"success": True, "data": result}}
except Exception as e:
return {{"success": False, "message": str(e)}}
""",
"data_model": """
class {model_name}(BaseModel):
\"\"\"{model_name}数据模型\"\"\"
def __init__(self{field_params}):
{field_initializations}
def to_dict(self):
\"\"\"转换为字典\"\"\"
return {
{field_dicts}
}
@classmethod
def from_dict(cls, data):
\"\"\"从字典创建实例\"\"\"
return cls({field_from_dicts})
"""
}
def generate_crud_controller(self, model_name):
"""生成CRUD控制器"""
template = self.templates["crud_controller"]
return template.format(model_name=model_name)
def generate_data_model(self, model_name, fields):
"""生成数据模型"""
template = self.templates["data_model"]
# 生成字段参数
field_params = ", " + ", ".join([f"{field_name}=None" for field_name in fields]) if fields else ""
# 生成字段初始化
field_initializations = "\n ".join([f"self.{field_name} = {field_name}" for field_name in fields])
# 生成字段字典
field_dicts = ",\n ".join([f"'{field_name}': self.{field_name}" for field_name in fields])
# 生成从字典创建实例的参数
field_from_dicts = ", ".join([f"data.get('{field_name}')" for field_name in fields])
return template.format(
model_name=model_name,
field_params=field_params,
field_initializations=field_initializations,
field_dicts=field_dicts,
field_from_dicts=field_from_dicts
)
# 使用示例
generator = TemplateBasedGenerator()
# 生成用户控制器
user_controller = generator.generate_crud_controller("User")
print("生成的User控制器:")
print(user_controller)
# 生成用户数据模型
user_model = generator.generate_data_model("User", ["id", "name", "email", "created_at"])
print("\n生成的User数据模型:")
print(user_model)
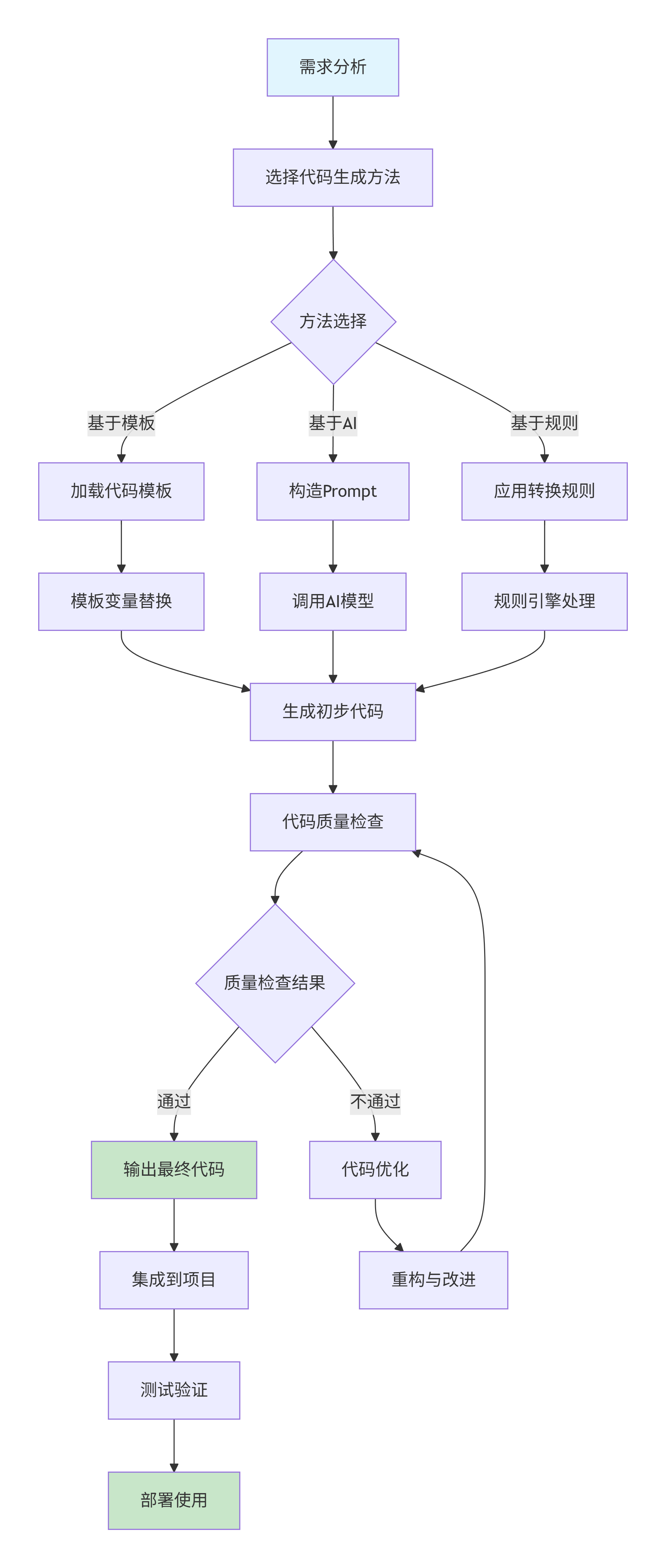
1.3 自动化代码生成流程图
graph TD
A[需求分析] --> B[选择代码生成方法]
B --> C{方法选择}
C -->|基于模板| D[加载代码模板]
C -->|基于AI| E[构造Prompt]
C -->|基于规则| F[应用转换规则]
D --> G[模板变量替换]
E --> H[调用AI模型]
F --> I[规则引擎处理]
G --> J[生成初步代码]
H --> J
I --> J
J --> K[代码质量检查]
K --> L{质量检查结果}
L -->|通过| M[输出最终代码]
L -->|不通过| N[代码优化]
N --> O[重构与改进]
O --> K
M --> P[集成到项目]
P --> Q[测试验证]
Q --> R[部署使用]
style A fill:#e1f5fe
style M fill:#c8e6c9
style R fill:#c8e6c9
1.4 自动化测试代码生成
python
# 示例:自动化测试代码生成
import ast
import inspect
class TestGenerator:
def __init__(self):
self.test_templates = self.load_test_templates()
def load_test_templates(self):
"""加载测试模板"""
return {
"unit_test": """
import pytest
from {module_path} import {function_name}
class Test{FunctionName}:
\"\"\"{function_name}函数的单元测试\"\"\"
def test_{function_name}_normal_case(self):
\"\"\"测试正常情况\"\"\"
# 准备测试数据
{test_data_preparation}
# 调用被测函数
result = {function_name}({test_arguments})
# 验证结果
{assertions}
def test_{function_name}_edge_case(self):
\"\"\"测试边界情况\"\"\"
# 准备边界测试数据
{edge_case_data}
# 调用被测函数
result = {function_name}({edge_case_arguments})
# 验证边界情况结果
{edge_case_assertions}
def test_{function_name}_error_case(self):
\"\"\"测试异常情况\"\"\"
# 准备异常测试数据
{error_case_data}
# 验证异常抛出
with pytest.raises({expected_exception}):
{function_name}({error_case_arguments})
""",
"integration_test": """
import pytest
from {module_path} import {class_name}
class Test{ClassName}Integration:
\"\"\"{class_name}集成测试\"\"\"
@pytest.fixture
def setup_{class_name_lower}(self):
\"\"\"测试夹具\"\"\"
instance = {class_name}()
yield instance
# 清理资源
instance.cleanup()
def test_integration_flow(self, setup_{class_name_lower}):
\"\"\"测试完整流程\"\"\"
instance = setup_{class_name_lower}
# 执行完整流程
{integration_steps}
# 验证最终状态
{final_assertions}
"""
}
def analyze_function(self, func):
"""分析函数结构"""
source = inspect.getsource(func)
tree = ast.parse(source)
function_info = {
'name': func.__name__,
'args': [],
'returns': None,
'docstring': ast.get_docstring(tree)
}
for node in ast.walk(tree):
if isinstance(node, ast.FunctionDef):
function_info['args'] = [arg.arg for arg in node.args.args]
# 简化处理,实际应用中需要更复杂的分析
return function_info
def generate_unit_test(self, func, module_path):
"""生成单元测试"""
func_info = self.analyze_function(func)
template = self.test_templates["unit_test"]
# 根据函数信息生成测试数据
test_data = self.generate_test_data(func_info)
return template.format(
module_path=module_path,
function_name=func_info['name'],
FunctionName=func_info['name'].title(),
test_data_preparation=test_data['preparation'],
test_arguments=test_data['arguments'],
assertions=test_data['assertions'],
edge_case_data=test_data['edge_preparation'],
edge_case_arguments=test_data['edge_arguments'],
edge_case_assertions=test_data['edge_assertions'],
error_case_data=test_data['error_preparation'],
expected_exception="Exception", # 简化处理
error_case_arguments=test_data['error_arguments']
)
def generate_test_data(self, func_info):
"""生成测试数据(简化版)"""
# 在实际应用中,这里需要更复杂的逻辑来生成合适的测试数据
return {
'preparation': "# 测试数据准备",
'arguments': ", ".join([f"test_{arg}" for arg in func_info['args']]),
'assertions': "assert result is not None",
'edge_preparation': "# 边界测试数据",
'edge_arguments': ", ".join([f"edge_{arg}" for arg in func_info['args']]),
'edge_assertions': "assert result is not None",
'error_preparation': "# 异常测试数据",
'error_arguments': ", ".join([f"invalid_{arg}" for arg in func_info['args']])
}
# 示例函数
def calculate_bmi(weight, height):
"""
计算BMI指数
Args:
weight: 体重(kg)
height: 身高(m)
Returns:
BMI值
"""
if height <= 0:
raise ValueError("身高必须大于0")
return weight / (height ** 2)
# 使用示例
test_gen = TestGenerator()
test_code = test_gen.generate_unit_test(calculate_bmi, "health_calculator")
print("生成的测试代码:")
print(test_code)
2. 低代码/无代码开发
2.1 低代码平台核心架构
python
# 示例:低代码平台核心组件
class LowCodePlatform:
def __init__(self):
self.components = {}
self.data_sources = {}
self.workflows = {}
self.ui_builder = UIBuilder()
self.data_manager = DataManager()
self.workflow_engine = WorkflowEngine()
def register_component(self, name, component):
"""注册组件"""
self.components[name] = component
def create_application(self, app_config):
"""根据配置创建应用"""
app = Application(app_config['name'])
# 创建数据模型
for model_config in app_config.get('data_models', []):
data_model = self.data_manager.create_model(model_config)
app.add_data_model(data_model)
# 创建页面
for page_config in app_config.get('pages', []):
page = self.ui_builder.build_page(page_config, self.components)
app.add_page(page)
# 创建工作流
for workflow_config in app_config.get('workflows', []):
workflow = self.workflow_engine.create_workflow(workflow_config)
app.add_workflow(workflow)
return app
class UIBuilder:
def __init__(self):
self.layout_templates = self.load_layout_templates()
def build_page(self, page_config, components):
"""构建页面"""
page = Page(page_config['name'])
# 设置布局
layout = self.create_layout(page_config.get('layout', 'default'))
page.set_layout(layout)
# 添加组件
for component_config in page_config.get('components', []):
component = self.create_component(component_config, components)
page.add_component(component)
return page
def create_layout(self, layout_type):
"""创建布局"""
template = self.layout_templates.get(layout_type, self.layout_templates['default'])
return Layout(template)
def create_component(self, config, available_components):
"""创建组件"""
component_type = config['type']
if component_type not in available_components:
raise ValueError(f"未知组件类型: {component_type}")
component_class = available_components[component_type]
return component_class(config.get('properties', {}))
class DataManager:
def create_model(self, model_config):
"""创建数据模型"""
model = DataModel(model_config['name'])
for field_config in model_config.get('fields', []):
field = DataField(
field_config['name'],
field_config['type'],
field_config.get('constraints', {})
)
model.add_field(field)
return model
class WorkflowEngine:
def create_workflow(self, workflow_config):
"""创建工作流"""
workflow = Workflow(workflow_config['name'])
for step_config in workflow_config.get('steps', []):
step = WorkflowStep(
step_config['name'],
step_config['action'],
step_config.get('conditions', [])
)
workflow.add_step(step)
return workflow
# 基础组件类
class Component:
def __init__(self, properties):
self.properties = properties
self.events = {}
def render(self):
"""渲染组件"""
raise NotImplementedError
def bind_event(self, event_name, handler):
"""绑定事件处理"""
self.events[event_name] = handler
class Button(Component):
def render(self):
return f"<button onclick='handleButtonClick()'>{self.properties.get('text', '按钮')}</button>"
class Input(Component):
def render(self):
return f"<input type='{self.properties.get('type', 'text')}' placeholder='{self.properties.get('placeholder', '')}'>"
class DataTable(Component):
def render(self):
return f"<table data-source='{self.properties.get('dataSource', '')}'></table>"
# 使用示例
platform = LowCodePlatform()
# 注册组件
platform.register_component('button', Button)
platform.register_component('input', Input)
platform.register_component('dataTable', DataTable)
# 应用配置
app_config = {
'name': '员工管理系统',
'data_models': [
{
'name': 'Employee',
'fields': [
{'name': 'id', 'type': 'integer', 'constraints': {'primary_key': True}},
{'name': 'name', 'type': 'string', 'constraints': {'required': True}},
{'name': 'department', 'type': 'string'},
{'name': 'salary', 'type': 'decimal'}
]
}
],
'pages': [
{
'name': '员工列表',
'layout': 'sidebar',
'components': [
{'type': 'dataTable', 'properties': {'dataSource': 'Employee'}},
{'type': 'button', 'properties': {'text': '添加员工', 'action': 'addEmployee'}}
]
}
],
'workflows': [
{
'name': '添加员工流程',
'steps': [
{'name': '验证数据', 'action': 'validateEmployeeData'},
{'name': '保存到数据库', 'action': 'saveEmployee'},
{'name': '发送通知', 'action': 'sendNotification'}
]
}
]
}
# 创建应用
# employee_app = platform.create_application(app_config)
2.2 可视化编程界面
python
# 示例:可视化编程界面模拟
class VisualProgrammingInterface:
def __init__(self):
self.canvas = Canvas()
self.toolbox = Toolbox()
self.property_panel = PropertyPanel()
self.code_generator = CodeGenerator()
def drag_component(self, component_type, position):
"""拖放组件到画布"""
component = self.toolbox.get_component(component_type)
self.canvas.add_component(component, position)
def connect_components(self, source_id, target_id, connection_type):
"""连接组件"""
self.canvas.create_connection(source_id, target_id, connection_type)
def update_properties(self, component_id, properties):
"""更新组件属性"""
component = self.canvas.get_component(component_id)
component.update_properties(properties)
self.property_panel.refresh(component)
def generate_code(self):
"""生成代码"""
application_structure = self.canvas.get_application_structure()
return self.code_generator.generate(application_structure)
def preview_application(self):
"""预览应用"""
code = self.generate_code()
return ApplicationPreview(code)
class Canvas:
def __init__(self):
self.components = {}
self.connections = []
self.next_id = 1
def add_component(self, component, position):
"""添加组件"""
component_id = f"comp_{self.next_id}"
self.next_id += 1
component.id = component_id
component.position = position
self.components[component_id] = component
return component_id
def create_connection(self, source_id, target_id, connection_type):
"""创建连接"""
connection = {
'source': source_id,
'target': target_id,
'type': connection_type
}
self.connections.append(connection)
def get_application_structure(self):
"""获取应用结构"""
return {
'components': self.components,
'connections': self.connections
}
class Toolbox:
def __init__(self):
self.categories = {
'UI组件': ['按钮', '输入框', '表格', '表单', '图表'],
'数据操作': ['查询', '过滤', '排序', '聚合'],
'逻辑控制': '条件判断', '循环', '事件处理'],
'集成服务': ['API调用', '数据库操作', '文件处理']
}
def get_component(self, component_type):
"""获取组件实例"""
if component_type == '按钮':
return Button({})
elif component_type == '输入框':
return Input({})
elif component_type == '表格':
return DataTable({})
# 其他组件...
else:
raise ValueError(f"未知组件类型: {component_type}")
# 可视化编程流程图
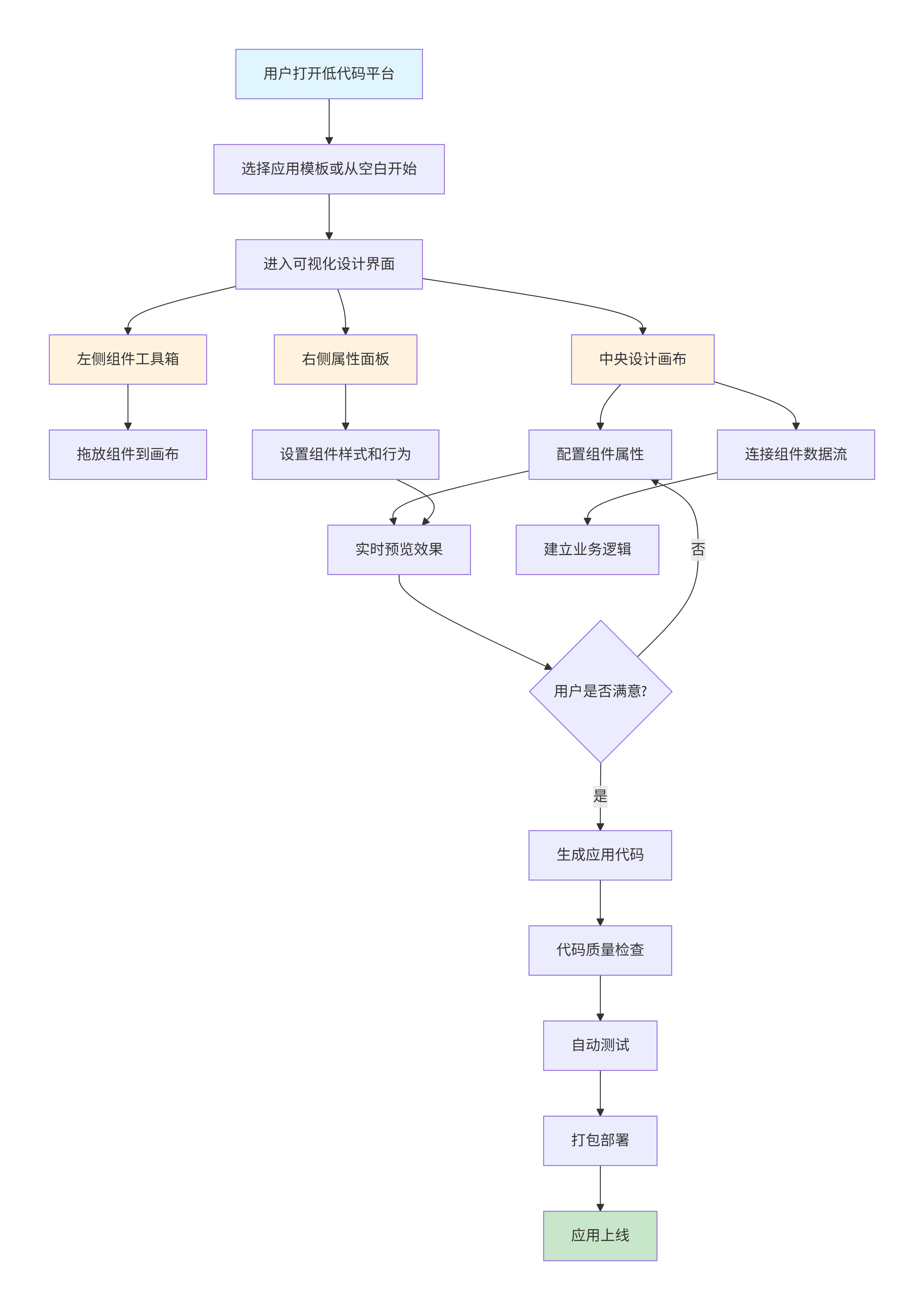
graph TD
A[用户打开低代码平台] --> B[选择应用模板或从空白开始]
B --> C[进入可视化设计界面]
C --> D[左侧组件工具箱]
C --> E[中央设计画布]
C --> F[右侧属性面板]
D --> G[拖放组件到画布]
E --> H[配置组件属性]
E --> I[连接组件数据流]
F --> J[设置组件样式和行为]
H --> K[实时预览效果]
I --> L[建立业务逻辑]
J --> K
K --> M{用户是否满意?}
M -->|否| H
M -->|是| N[生成应用代码]
N --> O[代码质量检查]
O --> P[自动测试]
P --> Q[打包部署]
Q --> R[应用上线]
style A fill:#e1f5fe
style R fill:#c8e6c9
style D fill:#fff3e0
style E fill:#fff3e0
style F fill:#fff3e0
2.3 无代码业务逻辑构建器
python
# 示例:无代码业务逻辑构建器
class NoCodeLogicBuilder:
def __init__(self):
self.actions = self.load_actions()
self.triggers = self.load_triggers()
self.conditions = self.load_conditions()
def load_actions(self):
"""加载可用的动作"""
return {
'send_email': {
'name': '发送邮件',
'parameters': ['收件人', '主题', '内容'],
'execute': self.send_email
},
'create_record': {
'name': '创建记录',
'parameters': ['数据模型', '字段数据'],
'execute': self.create_record
},
'update_record': {
'name': '更新记录',
'parameters': ['数据模型', '记录ID', '更新数据'],
'execute': self.update_record
},
'call_api': {
'name': '调用API',
'parameters': ['URL', '方法', '请求体', '头部'],
'execute': self.call_api
}
}
def load_triggers(self):
"""加载触发器"""
return {
'form_submit': '表单提交',
'button_click': '按钮点击',
'data_change': '数据变更',
'schedule': '定时触发',
'webhook': 'Webhook接收'
}
def load_conditions(self):
"""加载条件类型"""
return {
'equals': '等于',
'not_equals': '不等于',
'greater_than': '大于',
'less_than': '小于',
'contains': '包含',
'is_empty': '为空'
}
def build_workflow(self, workflow_config):
"""构建工作流"""
workflow = {
'name': workflow_config['name'],
'trigger': workflow_config['trigger'],
'conditions': [],
'actions': []
}
# 处理条件
for condition_config in workflow_config.get('conditions', []):
condition = self.build_condition(condition_config)
workflow['conditions'].append(condition)
# 处理动作
for action_config in workflow_config.get('actions', []):
action = self.build_action(action_config)
workflow['actions'].append(action)
return workflow
def build_condition(self, condition_config):
"""构建条件"""
return {
'field': condition_config['field'],
'operator': condition_config['operator'],
'value': condition_config['value']
}
def build_action(self, action_config):
"""构建动作"""
action_type = action_config['type']
if action_type not in self.actions:
raise ValueError(f"未知动作类型: {action_type}")
return {
'type': action_type,
'parameters': action_config.get('parameters', {})
}
def execute_workflow(self, workflow, context):
"""执行工作流"""
# 检查条件
if not self.check_conditions(workflow['conditions'], context):
return {"success": False, "message": "条件不满足"}
results = []
# 执行动作
for action in workflow['actions']:
try:
action_func = self.actions[action['type']]['execute']
result = action_func(action['parameters'], context)
results.append({
'action': action['type'],
'success': True,
'result': result
})
except Exception as e:
results.append({
'action': action['type'],
'success': False,
'error': str(e)
})
return {
"success": all([r['success'] for r in results]),
"results": results
}
def check_conditions(self, conditions, context):
"""检查条件"""
for condition in conditions:
field_value = context.get(condition['field'])
operator = condition['operator']
expected_value = condition['value']
if not self.evaluate_condition(field_value, operator, expected_value):
return False
return True
def evaluate_condition(self, actual_value, operator, expected_value):
"""评估条件"""
if operator == 'equals':
return actual_value == expected_value
elif operator == 'not_equals':
return actual_value != expected_value
elif operator == 'greater_than':
return actual_value > expected_value
elif operator == 'less_than':
return actual_value < expected_value
elif operator == 'contains':
return expected_value in actual_value
elif operator == 'is_empty':
return not actual_value
else:
return False
# 动作执行方法
def send_email(self, parameters, context):
"""发送邮件"""
# 实际实现会调用邮件服务
print(f"发送邮件给 {parameters['收件人']}: {parameters['主题']}")
return {"message_id": "mock_message_id"}
def create_record(self, parameters, context):
"""创建记录"""
model = parameters['数据模型']
data = parameters['字段数据']
print(f"在 {model} 中创建记录: {data}")
return {"record_id": "mock_record_id"}
def update_record(self, parameters, context):
"""更新记录"""
model = parameters['数据模型']
record_id = parameters['记录ID']
update_data = parameters['更新数据']
print(f"更新 {model} 中的记录 {record_id}: {update_data}")
return {"updated": True}
def call_api(self, parameters, context):
"""调用API"""
url = parameters['URL']
method = parameters.get('方法', 'GET')
print(f"调用API: {method} {url}")
return {"status_code": 200, "response": "mock_response"}
# 使用示例
logic_builder = NoCodeLogicBuilder()
# 构建一个工作流:当新用户注册时,发送欢迎邮件并创建用户档案
workflow_config = {
'name': '新用户注册流程',
'trigger': 'form_submit',
'conditions': [
{'field': 'form_type', 'operator': 'equals', 'value': 'user_registration'}
],
'actions': [
{
'type': 'send_email',
'parameters': {
'收件人': '{{email}}',
'主题': '欢迎加入我们!',
'内容': '亲爱的{{name}},感谢您注册我们的服务。'
}
},
{
'type': 'create_record',
'parameters': {
'数据模型': 'UserProfile',
'字段数据': {
'name': '{{name}}',
'email': '{{email}}',
'registration_date': '{{timestamp}}'
}
}
}
]
}
workflow = logic_builder.build_workflow(workflow_config)
print("构建的工作流:")
print(workflow)
# 执行工作流
context = {
'form_type': 'user_registration',
'name': '张三',
'email': 'zhangsan@example.com',
'timestamp': '2024-01-01 10:00:00'
}
# result = logic_builder.execute_workflow(workflow, context)
# print("执行结果:", result)
3. 算法优化实践
3.1 自动化算法选择与调优
python
# 示例:自动化机器学习流水线
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, cross_val_score, GridSearchCV
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, GradientBoostingClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, LabelEncoder
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
class AutoMLPipeline:
def __init__(self):
self.models = {
'random_forest': RandomForestClassifier(),
'gradient_boosting': GradientBoostingClassifier(),
'svm': SVC(),
'logistic_regression': LogisticRegression()
}
self.param_grids = {
'random_forest': {
'n_estimators': [50, 100, 200],
'max_depth': [None, 10, 20],
'min_samples_split': [2, 5, 10]
},
'gradient_boosting': {
'n_estimators': [50, 100, 200],
'learning_rate': [0.01, 0.1, 0.2],
'max_depth': [3, 5, 7]
},
'svm': {
'C': [0.1, 1, 10],
'kernel': ['linear', 'rbf'],
'gamma': ['scale', 'auto']
},
'logistic_regression': {
'C': [0.1, 1, 10],
'penalty': ['l1', 'l2'],
'solver': ['liblinear']
}
}
self.best_model = None
self.best_score = 0
self.best_params = {}
def load_data(self, file_path):
"""加载数据"""
if file_path.endswith('.csv'):
return pd.read_csv(file_path)
elif file_path.endswith('.xlsx'):
return pd.read_excel(file_path)
else:
raise ValueError("不支持的文件格式")
def preprocess_data(self, data, target_column):
"""数据预处理"""
# 分离特征和目标
X = data.drop(columns=[target_column])
y = data[target_column]
# 处理缺失值
X = X.fillna(X.mean())
# 编码分类变量
categorical_columns = X.select_dtypes(include=['object']).columns
for col in categorical_columns:
le = LabelEncoder()
X[col] = le.fit_transform(X[col])
# 如果目标是分类变量,进行编码
if y.dtype == 'object':
le = LabelEncoder()
y = le.fit_transform(y)
# 标准化特征
scaler = StandardScaler()
X = scaler.fit_transform(X)
return X, y, scaler
def evaluate_models(self, X, y):
"""评估所有模型"""
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
results = {}
for model_name, model in self.models.items():
print(f"正在评估模型: {model_name}")
# 使用网格搜索寻找最佳参数
grid_search = GridSearchCV(
model,
self.param_grids[model_name],
cv=5,
scoring='accuracy',
n_jobs=-1
)
grid_search.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 在测试集上评估
y_pred = grid_search.best_estimator_.predict(X_test)
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
results[model_name] = {
'best_params': grid_search.best_params_,
'best_score': grid_search.best_score_,
'test_accuracy': accuracy,
'model': grid_search.best_estimator_
}
# 更新最佳模型
if accuracy > self.best_score:
self.best_score = accuracy
self.best_model = grid_search.best_estimator_
self.best_params = grid_search.best_params_
return results
def feature_importance_analysis(self, model, feature_names):
"""特征重要性分析"""
if hasattr(model, 'feature_importances_'):
importances = model.feature_importances_
indices = np.argsort(importances)[::-1]
print("特征重要性排名:")
for i in range(min(10, len(feature_names))):
print(f"{i+1}. {feature_names[indices[i]]}: {importances[indices[i]]:.4f}")
return importances
else:
print("该模型不支持特征重要性分析")
return None
def generate_model_report(self, results):
"""生成模型报告"""
report = "# 自动化机器学习报告\n\n"
report += "## 模型性能比较\n\n"
report += "| 模型 | 最佳参数 | 交叉验证分数 | 测试集准确率 |\n"
report += "|------|----------|--------------|-------------|\n"
for model_name, result in results.items():
report += f"| {model_name} | {str(result['best_params'])[:50]}... | {result['best_score']:.4f} | {result['test_accuracy']:.4f} |\n"
report += f"\n## 最佳模型\n\n"
report += f"- **模型类型**: {type(self.best_model).__name__}\n"
report += f"- **最佳参数**: {self.best_params}\n"
report += f"- **测试集准确率**: {self.best_score:.4f}\n"
return report
# 使用示例
def demo_automl():
"""演示AutoML流水线"""
# 创建示例数据
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
# 生成分类数据集
X, y = make_classification(
n_samples=1000,
n_features=20,
n_informative=15,
n_redundant=5,
n_classes=3,
random_state=42
)
# 转换为DataFrame以便演示
feature_names = [f'feature_{i}' for i in range(20)]
data = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=feature_names)
data['target'] = y
# 创建和运行AutoML流水线
automl = AutoMLPipeline()
# 数据预处理
X_processed, y_processed, scaler = automl.preprocess_data(data, 'target')
# 评估模型
results = automl.evaluate_models(X_processed, y_processed)
# 生成报告
report = automl.generate_model_report(results)
print(report)
# 特征重要性分析
if hasattr(automl.best_model, 'feature_importances_'):
automl.feature_importance_analysis(automl.best_model, feature_names)
# 运行演示
demo_automl()
3.2 深度学习模型自动化优化
python
# 示例:深度学习模型自动化优化
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class DeepLearningOptimizer:
def __init__(self, input_shape, num_classes):
self.input_shape = input_shape
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.model = None
self.history = None
def create_model(self, architecture_config):
"""根据配置创建模型"""
model = keras.Sequential()
# 输入层
model.add(layers.Input(shape=self.input_shape))
# 隐藏层
for layer_config in architecture_config['hidden_layers']:
layer_type = layer_config['type']
if layer_type == 'dense':
model.add(layers.Dense(
units=layer_config['units'],
activation=layer_config.get('activation', 'relu')
))
elif layer_type == 'conv2d':
model.add(layers.Conv2D(
filters=layer_config['filters'],
kernel_size=layer_config['kernel_size'],
activation=layer_config.get('activation', 'relu')
))
elif layer_type == 'lstm':
model.add(layers.LSTM(
units=layer_config['units'],
return_sequences=layer_config.get('return_sequences', False)
))
# 添加正则化
if layer_config.get('dropout', 0) > 0:
model.add(layers.Dropout(layer_config['dropout']))
# 输出层
if self.num_classes == 2:
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
loss = 'binary_crossentropy'
else:
model.add(layers.Dense(self.num_classes, activation='softmax'))
loss = 'sparse_categorical_crossentropy'
# 编译模型
model.compile(
optimizer=architecture_config.get('optimizer', 'adam'),
loss=loss,
metrics=['accuracy']
)
self.model = model
return model
def hyperparameter_tuning(self, X_train, y_train, X_val, y_val, search_space):
"""超参数调优"""
best_score = 0
best_config = None
# 简化版的网格搜索
for learning_rate in search_space['learning_rates']:
for batch_size in search_space['batch_sizes']:
for hidden_units in search_space['hidden_units']:
for dropout_rate in search_space['dropout_rates']:
# 创建模型配置
config = {
'hidden_layers': [
{
'type': 'dense',
'units': hidden_units,
'activation': 'relu',
'dropout': dropout_rate
},
{
'type': 'dense',
'units': hidden_units // 2,
'activation': 'relu',
'dropout': dropout_rate
}
],
'optimizer': keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate)
}
# 创建和训练模型
model = self.create_model(config)
history = model.fit(
X_train, y_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=10,
validation_data=(X_val, y_val),
verbose=0
)
# 评估模型
val_accuracy = max(history.history['val_accuracy'])
if val_accuracy > best_score:
best_score = val_accuracy
best_config = {
'learning_rate': learning_rate,
'batch_size': batch_size,
'hidden_units': hidden_units,
'dropout_rate': dropout_rate,
'val_accuracy': val_accuracy
}
print(f"LR: {learning_rate}, BS: {batch_size}, HU: {hidden_units}, "
f"DR: {dropout_rate}, Val Acc: {val_accuracy:.4f}")
return best_config
def train_with_early_stopping(self, X_train, y_train, X_val, y_val,
epochs=100, patience=10):
"""使用早停法训练模型"""
early_stopping = keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(
monitor='val_loss',
patience=patience,
restore_best_weights=True
)
reduce_lr = keras.callbacks.ReduceLROnPlateau(
monitor='val_loss',
factor=0.2,
patience=5,
min_lr=1e-7
)
self.history = self.model.fit(
X_train, y_train,
batch_size=32,
epochs=epochs,
validation_data=(X_val, y_val),
callbacks=[early_stopping, reduce_lr],
verbose=1
)
return self.history
def visualize_training(self):
"""可视化训练过程"""
if self.history is None:
print("没有训练历史可可视化")
return
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 4))
# 准确率曲线
ax1.plot(self.history.history['accuracy'], label='训练准确率')
ax1.plot(self.history.history['val_accuracy'], label='验证准确率')
ax1.set_title('模型准确率')
ax1.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax1.set_ylabel('Accuracy')
ax1.legend()
# 损失曲线
ax2.plot(self.history.history['loss'], label='训练损失')
ax2.plot(self.history.history['val_loss'], label='验证损失')
ax2.set_title('模型损失')
ax2.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax2.set_ylabel('Loss')
ax2.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
def model_interpretation(self, X_sample, feature_names=None):
"""模型解释(简化版)"""
if feature_names is None:
feature_names = [f'Feature_{i}' for i in range(X_sample.shape[1])]
# 获取预测概率
predictions = self.model.predict(X_sample)
# 对于分类问题,分析预测置信度
if predictions.shape[1] > 1:
confidence = np.max(predictions, axis=1)
predicted_class = np.argmax(predictions, axis=1)
else:
confidence = predictions.flatten()
predicted_class = (predictions > 0.5).astype(int).flatten()
interpretation = {
'predictions': predictions,
'confidence': confidence,
'predicted_class': predicted_class
}
return interpretation
# 使用示例
def demo_dl_optimization():
"""演示深度学习优化"""
# 加载MNIST数据集
(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
# 数据预处理
X_train = X_train.reshape(-1, 28*28).astype('float32') / 255.0
X_test = X_test.reshape(-1, 28*28).astype('float32') / 255.0
# 划分验证集
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(
X_train, y_train, test_size=0.2, random_state=42
)
# 创建优化器
optimizer = DeepLearningOptimizer(input_shape=(784,), num_classes=10)
# 定义超参数搜索空间
search_space = {
'learning_rates': [1e-3, 1e-4],
'batch_sizes': [32, 64],
'hidden_units': [128, 256],
'dropout_rates': [0.2, 0.5]
}
# 超参数调优(在实际应用中可能需要更长时间)
print("开始超参数调优...")
best_config = optimizer.hyperparameter_tuning(
X_train, y_train, X_val, y_val, search_space
)
print(f"\n最佳配置: {best_config}")
# 使用最佳配置创建最终模型
final_config = {
'hidden_layers': [
{
'type': 'dense',
'units': best_config['hidden_units'],
'activation': 'relu',
'dropout': best_config['dropout_rate']
},
{
'type': 'dense',
'units': best_config['hidden_units'] // 2,
'activation': 'relu',
'dropout': best_config['dropout_rate']
}
],
'optimizer': keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=best_config['learning_rate'])
}
final_model = optimizer.create_model(final_config)
# 训练最终模型
print("\n训练最终模型...")
history = optimizer.train_with_early_stopping(
X_train, y_train, X_val, y_val, epochs=50, patience=10
)
# 评估模型
test_loss, test_accuracy = final_model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=0)
print(f"\n测试集准确率: {test_accuracy:.4f}")
# 可视化训练过程
optimizer.visualize_training()
return optimizer, test_accuracy
# 由于MNIST数据集较大,训练需要时间,这里只展示代码结构
# 在实际应用中可以根据需要运行
print("深度学习优化器代码示例已准备就绪")
3.3 算法优化流程图
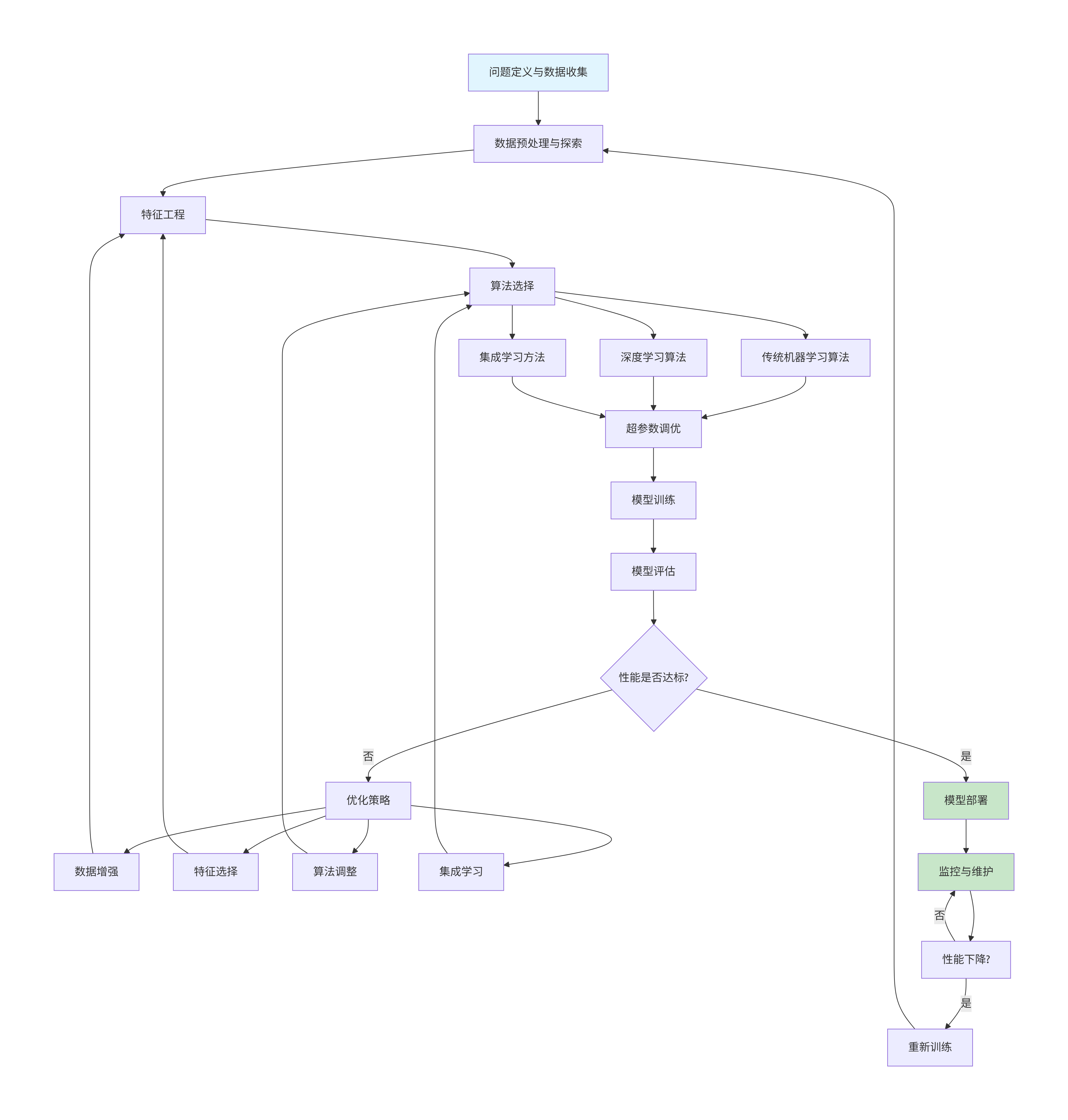
graph TD
A[问题定义与数据收集] --> B[数据预处理与探索]
B --> C[特征工程]
C --> D[算法选择]
D --> E[传统机器学习算法]
D --> F[深度学习算法]
D --> G[集成学习方法]
E --> H[超参数调优]
F --> H
G --> H
H --> I[模型训练]
I --> J[模型评估]
J --> K{性能是否达标?}
K -->|否| L[优化策略]
K -->|是| M[模型部署]
L --> N[数据增强]
L --> O[特征选择]
L --> P[算法调整]
L --> Q[集成学习]
N --> C
O --> C
P --> D
Q --> D
M --> R[监控与维护]
R --> S[性能下降?]
S -->|是| T[重新训练]
S -->|否| R
T --> B
style A fill:#e1f5fe
style M fill:#c8e6c9
style R fill:#c8e6c9
4. 综合应用案例
4.1 智能代码审查与优化系统
python
# 示例:智能代码审查与优化系统
import ast
import astor
import radon
from radon.complexity import cc_visit
from radon.metrics import h_visit
import numpy as np
class IntelligentCodeReviewer:
def __init__(self):
self.rules = self.load_review_rules()
self.optimization_patterns = self.load_optimization_patterns()
def load_review_rules(self):
"""加载代码审查规则"""
return {
'complexity': {
'max_cyclomatic_complexity': 10,
'max_maintainability_index': 65,
'max_function_length': 50
},
'style': {
'naming_convention': True,
'docstring_required': True,
'max_parameters': 5
},
'security': {
'check_hardcoded_secrets': True,
'check_sql_injection': True,
'check_input_validation': True
},
'performance': {
'check_loop_optimization': True,
'check_memory_usage': True,
'check_algorithm_complexity': True
}
}
def load_optimization_patterns(self):
"""加载优化模式"""
return {
'loop_optimization': {
'pattern': 'for_loop_with_list_comprehension',
'replacement': 'list_comprehension',
'condition': 'simple_loop'
},
'function_extraction': {
'pattern': 'repeated_code_block',
'replacement': 'function_call',
'condition': 'code_repetition'
},
'algorithm_optimization': {
'pattern': 'inefficient_algorithm',
'replacement': 'optimized_algorithm',
'condition': 'high_time_complexity'
}
}
def review_code(self, code):
"""审查代码"""
issues = []
suggestions = []
try:
# 解析AST
tree = ast.parse(code)
# 分析代码复杂度
complexity_issues = self.analyze_complexity(code, tree)
issues.extend(complexity_issues)
# 检查代码风格
style_issues = self.check_style(tree)
issues.extend(style_issues)
# 安全检查
security_issues = self.check_security(tree)
issues.extend(security_issues)
# 性能检查
performance_issues = self.check_performance(tree)
issues.extend(performance_issues)
# 生成优化建议
suggestions = self.generate_optimization_suggestions(tree, issues)
except SyntaxError as e:
issues.append({
'type': 'syntax_error',
'message': f'语法错误: {e}',
'line': e.lineno,
'severity': 'high'
})
return {
'issues': issues,
'suggestions': suggestions,
'summary': self.generate_summary(issues)
}
def analyze_complexity(self, code, tree):
"""分析代码复杂度"""
issues = []
# 使用radon分析圈复杂度
complexities = cc_visit(code)
for complexity in complexities:
if complexity.complexity > self.rules['complexity']['max_cyclomatic_complexity']:
issues.append({
'type': 'high_complexity',
'message': f'函数 {complexity.name} 的圈复杂度较高: {complexity.complexity}',
'line': complexity.lineno,
'severity': 'medium',
'suggestion': '考虑将函数拆分为更小的函数'
})
# 分析可维护性指数
maintainability = h_visit(code)
if maintainability < self.rules['complexity']['max_maintainability_index']:
issues.append({
'type': 'low_maintainability',
'message': f'代码可维护性指数较低: {maintainability}',
'line': 1,
'severity': 'medium',
'suggestion': '提高代码可读性和模块化程度'
})
return issues
def check_style(self, tree):
"""检查代码风格"""
issues = []
for node in ast.walk(tree):
# 检查函数参数数量
if isinstance(node, ast.FunctionDef):
if len(node.args.args) > self.rules['style']['max_parameters']:
issues.append({
'type': 'too_many_parameters',
'message': f'函数 {node.name} 参数过多: {len(node.args.args)}',
'line': node.lineno,
'severity': 'low',
'suggestion': '考虑使用对象或字典来组织参数'
})
# 检查文档字符串
if self.rules['style']['docstring_required'] and not ast.get_docstring(node):
issues.append({
'type': 'missing_docstring',
'message': f'函数 {node.name} 缺少文档字符串',
'line': node.lineno,
'severity': 'low',
'suggestion': '添加函数文档字符串'
})
return issues
def check_security(self, tree):
"""安全检查"""
issues = []
for node in ast.walk(tree):
# 检查硬编码的密码或密钥
if isinstance(node, ast.Str):
if self.is_potential_secret(node.s):
issues.append({
'type': 'hardcoded_secret',
'message': '发现可能硬编码的密码或密钥',
'line': node.lineno,
'severity': 'high',
'suggestion': '将密码或密钥移到环境变量或配置文件中'
})
# 检查SQL注入风险
if isinstance(node, ast.Call):
if (isinstance(node.func, ast.Attribute) and
node.func.attr == 'execute' and
self.contains_string_formatting(node.args[0] if node.args else None)):
issues.append({
'type': 'sql_injection_risk',
'message': '发现可能的SQL注入风险',
'line': node.lineno,
'severity': 'high',
'suggestion': '使用参数化查询或ORM'
})
return issues
def check_performance(self, tree):
"""性能检查"""
issues = []
for node in ast.walk(tree):
# 检查嵌套循环
if isinstance(node, ast.For):
parent = self.get_parent_node(tree, node)
if parent and isinstance(parent, ast.For):
issues.append({
'type': 'nested_loop',
'message': '发现嵌套循环,可能影响性能',
'line': node.lineno,
'severity': 'medium',
'suggestion': '考虑使用更高效的算法或向量化操作'
})
# 检查在循环中调用昂贵操作
if isinstance(node, ast.Call) and self.is_in_loop(tree, node):
if self.is_expensive_operation(node):
issues.append({
'type': 'expensive_operation_in_loop',
'message': '在循环中执行昂贵操作',
'line': node.lineno,
'severity': 'medium',
'suggestion': '将昂贵操作移到循环外部'
})
return issues
def generate_optimization_suggestions(self, tree, issues):
"""生成优化建议"""
suggestions = []
# 基于问题生成具体建议
for issue in issues:
if issue['type'] == 'high_complexity':
suggestions.append({
'type': 'refactor_function',
'description': f"重构函数以降低复杂度",
'priority': 'medium',
'estimated_effort': '中等'
})
elif issue['type'] == 'nested_loop':
suggestions.append({
'type': 'optimize_algorithm',
'description': "优化算法以减少嵌套循环",
'priority': 'high',
'estimated_effort': '高'
})
elif issue['type'] == 'sql_injection_risk':
suggestions.append({
'type': 'security_fix',
'description': "修复SQL注入漏洞",
'priority': 'critical',
'estimated_effort': '低'
})
return suggestions
def generate_summary(self, issues):
"""生成摘要"""
severity_count = {
'critical': 0,
'high': 0,
'medium': 0,
'low': 0
}
for issue in issues:
severity_count[issue['severity']] += 1
return {
'total_issues': len(issues),
'severity_breakdown': severity_count,
'quality_score': self.calculate_quality_score(issues)
}
def calculate_quality_score(self, issues):
"""计算代码质量分数"""
if not issues:
return 100
# 基于问题严重程度计算分数
penalty = 0
for issue in issues:
if issue['severity'] == 'critical':
penalty += 10
elif issue['severity'] == 'high':
penalty += 5
elif issue['severity'] == 'medium':
penalty += 2
elif issue['severity'] == 'low':
penalty += 1
return max(0, 100 - penalty)
# 辅助方法
def is_potential_secret(self, s):
"""检查字符串是否可能是密码或密钥"""
secret_keywords = ['password', 'secret', 'key', 'token', 'api_key']
return any(keyword in s.lower() for keyword in secret_keywords) and len(s) > 8
def contains_string_formatting(self, node):
"""检查节点是否包含字符串格式化"""
if node is None:
return False
return isinstance(node, ast.BinOp) and isinstance(node.op, ast.Mod)
def get_parent_node(self, tree, target_node):
"""获取父节点"""
for parent in ast.walk(tree):
for child in ast.iter_child_nodes(parent):
if child is target_node:
return parent
return None
def is_in_loop(self, tree, node):
"""检查节点是否在循环中"""
current = node
while hasattr(current, 'parent'):
if isinstance(current, (ast.For, ast.While)):
return True
current = getattr(current, 'parent', None)
return False
def is_expensive_operation(self, node):
"""检查是否是昂贵操作"""
expensive_functions = ['requests.get', 'requests.post', 'open', 'eval', 'exec']
if isinstance(node.func, ast.Attribute):
func_name = f"{node.func.value.id}.{node.func.attr}" if hasattr(node.func.value, 'id') else node.func.attr
return func_name in expensive_functions
return False
# 使用示例
def demo_code_review():
"""演示代码审查"""
sample_code = """
import sqlite3
def get_user_data(user_id):
conn = sqlite3.connect('database.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 潜在的SQL注入风险
query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = %s" % user_id
cursor.execute(query)
results = cursor.fetchall()
# 嵌套循环示例
for user in results:
for detail in user:
print(detail)
conn.close()
return results
def complex_function(a, b, c, d, e, f, g):
# 参数过多的函数
result = 0
for i in range(100):
for j in range(100):
for k in range(100):
result += i * j * k
return result
"""
reviewer = IntelligentCodeReviewer()
review_result = reviewer.review_code(sample_code)
print("代码审查结果:")
print(f"总问题数: {review_result['summary']['total_issues']}")
print(f"质量分数: {review_result['summary']['quality_score']}")
print("\n详细问题:")
for issue in review_result['issues']:
print(f"- [{issue['severity'].upper()}] {issue['message']} (行 {issue['line']})")
print(f" 建议: {issue['suggestion']}")
print("\n优化建议:")
for suggestion in review_result['suggestions']:
print(f"- [{suggestion['priority']}] {suggestion['description']} (预计工作量: {suggestion['estimated_effort']})")
# 运行演示
demo_code_review()
5. 未来发展趋势
5.1 AI编程的发展方向
python
# 示例:AI编程未来发展趋势分析
class AIProgrammingTrends:
def __init__(self):
self.trends = self.analyze_trends()
def analyze_trends(self):
"""分析AI编程发展趋势"""
return {
'code_generation': {
'current_state': '基础代码生成和补全',
'future_direction': '全栈应用生成',
'timeline': '2-5年',
'impact': '高',
'key_technologies': ['大语言模型', '程序合成', '代码理解']
},
'low_code_platforms': {
'current_state': '企业级应用开发',
'future_direction': '公民开发者普及',
'timeline': '3-5年',
'impact': '中高',
'key_technologies': ['可视化编程', 'DSL', 'AI辅助设计']
},
'algorithm_optimization': {
'current_state': '特定领域优化',
'future_direction': '全自动算法设计',
'timeline': '5-10年',
'impact': '极高',
'key_technologies': ['强化学习', '元学习', '神经架构搜索']
},
'testing_automation': {
'current_state': '测试用例生成',
'future_direction': '自主测试系统',
'timeline': '3-7年',
'impact': '高',
'key_technologies': ['形式化验证', '模糊测试', 'AI测试代理']
},
'devops_intelligence': {
'current_state': '基础监控和预警',
'future_direction': '自修复系统',
'timeline': '5-8年',
'impact': '中高',
'key_technologies': ['AIOps', '因果推理', '自动根因分析']
}
}
def generate_roadmap(self, focus_area):
"""生成技术发展路线图"""
if focus_area not in self.trends:
return None
trend = self.trends[focus_area]
roadmap = {
'short_term': f"1-2年: 完善{trend['current_state']}",
'mid_term': f"2-5年: 实现{trend['future_direction']}的核心功能",
'long_term': f"5+年: 全面部署和优化,实现产业化应用"
}
return roadmap
def assess_impact(self, industry):
"""评估对特定行业的影响"""
impact_assessment = {
'finance': {
'benefits': ['自动化合规检查', '智能风险控制', '高效交易算法'],
'challenges': ['监管合规', '系统稳定性', '数据隐私'],
'adoption_timeline': '快速'
},
'healthcare': {
'benefits': ['医疗数据分析', '诊断辅助系统', '药物研发加速'],
'challenges': ['数据敏感性', '伦理考量', '验证复杂性'],
'adoption_timeline': '中等'
},
'manufacturing': {
'benefits': ['工艺优化', '质量控制', '预测性维护'],
'challenges': ['系统集成', '技术培训', '投资回报'],
'adoption_timeline': '中等'
},
'education': {
'benefits': ['个性化学习', '自动评分', '教育资源生成'],
'challenges': ['教学质量保证', '数字鸿沟', '教师培训'],
'adoption_timeline': '快速'
}
}
return impact_assessment.get(industry, {})
def generate_adoption_strategy(self, organization_size):
"""生成采用策略"""
strategies = {
'startup': {
'phase1': '聚焦核心业务需求的AI工具',
'phase2': '建立AI辅助开发流程',
'phase3': '全面集成AI编程实践',
'key_metrics': ['开发效率提升', '代码质量改善', '上市时间缩短']
},
'sme': {
'phase1': '试点项目和团队培训',
'phase2': '部门级推广和流程优化',
'phase3': '企业级AI编程平台',
'key_metrics': ['人力成本节约', '错误率降低', '客户满意度提升']
},
'enterprise': {
'phase1': '战略规划和概念验证',
'phase2': '平台建设和文化转型',
'phase3': '生态系统构建和创新加速',
'key_metrics': ['创新能力', '市场份额', '技术领导力']
}
}
return strategies.get(organization_size, {})
# 使用示例
trends_analyzer = AIProgrammingTrends()
print("AI编程主要发展趋势:")
for area, trend in trends_analyzer.trends.items():
print(f"\n{area.upper()}:")
print(f" 当前状态: {trend['current_state']}")
print(f" 未来方向: {trend['future_direction']}")
print(f" 时间线: {trend['timeline']}")
print(f" 影响程度: {trend['impact']}")
print("\n金融行业影响评估:")
finance_impact = trends_analyzer.assess_impact('finance')
print(f"主要益处: {', '.join(finance_impact['benefits'])}")
print(f"主要挑战: {', '.join(finance_impact['challenges'])}")
print("\n初创企业采用策略:")
startup_strategy = trends_analyzer.generate_adoption_strategy('startup')
for phase, action in startup_strategy.items():
if phase != 'key_metrics':
print(f"{phase}: {action}")
5.2 伦理考量与最佳实践
python
# 示例:AI编程伦理框架
class AIEthicsFramework:
def __init__(self):
self.principles = self.define_ethical_principles()
self.guidelines = self.develop_guidelines()
def define_ethical_principles(self):
"""定义伦理原则"""
return {
'transparency': {
'description': 'AI系统的决策过程应该透明可解释',
'requirements': [
'代码生成理由说明',
'算法选择依据文档化',
'数据来源和预处理记录'
]
},
'fairness': {
'description': '避免算法偏见和歧视',
'requirements': [
'偏见检测和缓解',
'多样化训练数据',
'公平性评估指标'
]
},
'accountability': {
'description': '明确AI系统的责任归属',
'requirements': [
'人工监督机制',
'错误追溯系统',
'责任分配框架'
]
},
'privacy': {
'description': '保护用户数据和隐私',
'requirements': [
'数据最小化原则',
'隐私保护技术',
'合规性检查'
]
},
'safety': {
'description': '确保AI系统的安全可靠',
'requirements': [
'鲁棒性测试',
'安全边界设置',
'故障安全机制'
]
}
}
def develop_guidelines(self):
"""制定实施指南"""
return {
'code_generation': {
'review_requirement': '所有AI生成代码必须经过人工审查',
'documentation': '记录代码生成的目的和修改历史',
'testing': '生成代码必须通过完整的测试套件'
},
'model_training': {
'data_provenance': '记录训练数据的来源和处理过程',
'bias_audit': '定期进行偏见和公平性审计',
'performance_monitoring': '持续监控模型性能和行为'
},
'deployment': {
'human_oversight': '关键系统必须有人工监督机制',
'rollback_plan': '制定系统回滚计划',
'impact_assessment': '评估系统对用户和社会的潜在影响'
}
}
def ethics_checklist(self, project_type):
"""伦理检查清单"""
checklists = {
'code_generation': [
'是否清楚说明代码生成的目的和限制?',
'是否经过适当的安全审查?',
'是否包含适当的错误处理?',
'是否遵循可访问性标准?',
'是否考虑隐私影响?'
],
'algorithm_design': [
'是否测试过算法在不同群体间的公平性?',
'是否能够解释算法的决策过程?',
'是否有防止误用的机制?',
'是否考虑环境和社会影响?',
'是否有定期审计计划?'
],
'data_processing': [
'数据收集是否获得适当同意?',
'是否最小化收集个人数据?',
'是否有数据安全保护措施?',
'是否允许用户访问和删除数据?',
'是否符合相关数据保护法规?'
]
}
return checklists.get(project_type, [])
def risk_assessment(self, ai_system):
"""风险评估框架"""
risks = {
'technical': {
'system_failure': '系统故障导致服务中断',
'security_vulnerability': '安全漏洞被利用',
'performance_degradation': '性能下降影响用户体验'
},
'ethical': {
'algorithmic_bias': '算法决策存在偏见',
'lack_of_transparency': '决策过程不透明',
'privacy_violation': '侵犯用户隐私'
},
'social': {
'job_displacement': '自动化导致工作岗位减少',
'information_manipulation': '信息操纵和虚假内容',
'dependency_risk': '过度依赖AI系统'
}
}
return risks
def generate_ethics_report(self, project_details):
"""生成伦理报告"""
report = f"""
# AI系统伦理评估报告
## 项目概述
- 项目名称: {project_details.get('name', '未指定')}
- 项目类型: {project_details.get('type', '未指定')}
- 评估日期: {project_details.get('date', '未指定')}
## 伦理原则符合性评估
{self.assess_principles_compliance(project_details)}
## 风险识别与缓解
{self.identify_risks(project_details)}
## 建议与改进措施
{self.generate_recommendations(project_details)}
## 结论
{self.generate_conclusion(project_details)}
"""
return report
def assess_principles_compliance(self, project_details):
"""评估原则符合性"""
# 简化实现
return "透明度: 部分符合\n公平性: 符合\n问责制: 符合\n隐私保护: 需要改进\n安全性: 符合"
def identify_risks(self, project_details):
"""识别风险"""
return "主要风险: 算法偏见可能性中等\n缓解措施: 增加多样性训练数据,建立定期审计机制"
def generate_recommendations(self, project_details):
"""生成建议"""
return "1. 加强隐私保护措施\n2. 建立用户反馈机制\n3. 进行第三方伦理审计"
def generate_conclusion(self, project_details):
"""生成结论"""
return "项目总体上符合伦理要求,建议在部署前解决已识别的隐私问题。"
# 使用示例
ethics_framework = AIEthicsFramework()
print("AI编程伦理原则:")
for principle, details in ethics_framework.principles.items():
print(f"\n{principle}:")
print(f" 描述: {details['description']}")
print(f" 要求: {', '.join(details['requirements'])}")
print("\n代码生成伦理检查清单:")
checklist = ethics_framework.ethics_checklist('code_generation')
for i, item in enumerate(checklist, 1):
print(f"{i}. {item}")
# 生成示例伦理报告
project_info = {
'name': '智能招聘系统',
'type': '算法决策系统',
'date': '2024-01-15'
}
ethics_report = ethics_framework.generate_ethics_report(project_info)
print("\n伦理评估报告示例:")
print(ethics_report)
结论
AI编程正在快速发展,自动化代码生成、低代码/无代码开发和算法优化实践已经成为现代软件开发的重要组成部分。通过这些技术,我们可以:
-
显著提高开发效率 - 自动化重复性任务,让开发者专注于创造性工作
-
降低技术门槛 - 使非专业开发者也能创建复杂的应用程序
-
优化系统性能 - 通过智能算法选择和改进提升应用质量
-
确保代码质量 - 通过自动化审查和测试减少人为错误
关键成功因素
-
数据质量:高质量的训练数据是AI编程成功的基础
-
人工监督:AI系统需要人类的指导和监督
-
持续学习:技术快速发展,需要不断更新知识和技能
-
伦理考量:在追求效率的同时不能忽视伦理和社会责任
未来展望
随着技术的不断进步,AI编程将在以下方面继续发展:
-
更智能的代码理解:AI将更好地理解代码的语义和上下文
-
全栈应用生成:从需求描述直接生成完整的应用程序
-
自主系统开发:AI系统能够自我改进和优化
-
跨平台适配:自动生成适用于不同平台和设备的代码
AI编程不是要取代开发者,而是成为开发者的强大助手,帮助我们构建更好、更可靠的软件系统。通过合理利用这些技术,我们可以迎接更加智能和高效的软件开发未来。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献88条内容
已为社区贡献88条内容








所有评论(0)